Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Two-Strain Tuberculosis Model (betts_10_133)¶
This is example 10.133 from John T.Betts, Practical Methods for Optimal Control Using NonlinearProgramming, 3rd edition, Chapter 10: Test Problems.
More details may be found in chapter 8.17 of this book.
States
\(S, T, L_1, I_1, L_", I_2\) : state variables
Controls
\(u_1, u_2\) : control variables
import numpy as np
import sympy as sm
import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
import time
from opty import Problem
from opty.utils import create_objective_function, MathJaxRepr
Equations of Motion.¶
start = time.time()
t = me.dynamicsymbols._t
S, T, L1, I1, L2, I2 = me.dynamicsymbols('S T L1 I1 L2 I2')
u1, u2 = me.dynamicsymbols('u1, u2')
beta1, d2, r2, betastar, beta2, k1, p, B1, nu, k2, q, B2, d1, r1, N = \
sm.symbols('beta1 d2 r2 betastar beta2 k1 p B1 nu k2 q B2 d1 r1 N')
Lambda = nu * N
eom = sm.Matrix([
-S.diff(t) + Lambda - beta1*S*I1/N - betastar*S*I2/N - nu*S,
-T.diff(t) + (u1*r1*L1 - nu*T + (1-(1-u2)*(p+q))*r2*I1 -
beta2*T*I1/N - betastar*T*I2/N),
-L1.diff(t) + (beta1*S*I1/N - (nu+k1)*L1 - u1*r1*L1 +
(1-u2)*p*r2*I1 + beta2*T*I1/N - betastar*L1*I2/N),
-L2.diff(t) + (1-u2)*q*r2*I1 - (nu+k2)*L2 + betastar*(S+L1+T)*I2/N,
-I1.diff(t) + k1*L1 - (nu+d1)*I1 - r2*I1,
-I2.diff(t) + k2*L2 - (nu+d2)*I2,
])
MathJaxRepr(eom)
Define and Solve the Optimization Problem¶
num_nodes = 801
t0, tf = 0.0, 5.0
interval_value = tf / (num_nodes - 1)
state_symbols = (S, T, L1, L2, I1, I2)
unkonwn_input_trajectories = (u1, u2)
par_map = {
beta1: 13,
d2: 0.0,
r2: 1.0,
betastar: 0.029,
beta2: 13,
k1: 0.5,
p: 0.4,
B1: 50,
nu: 0.0143,
k2: 1.0,
q: 0.1,
B2: 500,
d1: 0.0,
r1: 2.0,
N: 30000,
}
Specify the objective function and form the gradient.
objective = sm.Integral((L2 + I2 + 0.5*B1*u1**2 +
0.5*B2*u2**2).subs(par_map), t)
obj, obj_grad = create_objective_function(
objective,
state_symbols,
unkonwn_input_trajectories,
tuple(),
num_nodes,
interval_value,
)
Instance constraints and bounds.
instance_constraints = (
S.func(t0) - 76*par_map[N]/120,
T.func(t0) - par_map[N]/120,
L1.func(t0) - 36*par_map[N]/120,
I1.func(t0) - 4*par_map[N]/120,
L2.func(t0) - 2*par_map[N]/120,
I2.func(t0) - par_map[N]/120,
)
bounds = {
u1: (0.05, 0.95),
u2: (0.05, 0.95),
}
Create the optimization problem.
prob = Problem(
obj,
obj_grad,
eom,
state_symbols,
num_nodes,
interval_value,
instance_constraints=instance_constraints,
known_parameter_map=par_map,
bounds=bounds,
time_symbol=t,
)
Acceptable tolerance and iteration settings are lowered, to get convergence with a reasonable number of iterations.
prob.add_option('max_iter', 4000)
prob.add_option('acceptable_tol', 1e-2)
prob.add_option('acceptable_iter', 5)
Rough initial guess.
initial_guess = np.ones(prob.num_free)
Find the optimal solution.
start_solve = time.time()
solution, info = prob.solve(initial_guess)
end_solve = time.time()
print(f"Solve time: {end_solve - start_solve:.3f} seconds")
print(info['status_msg'])
Jstar = 5152.07310
print(f"Objective value achieved: {info['obj_val']:.4f}, ",
f"as per the book it is {Jstar:.4f}, so the deviation is: ",
f"{(info['obj_val'] - Jstar) / Jstar*100:.3f} %")
Tbstar = 1123
print(f"Individuals infected with resistant Tb = ",
f"{solution[4*num_nodes-1] + solution[6*num_nodes-1]:.3f}, ",
f"vs. {Tbstar} from the book, hence deviation: ",
f"{(solution[4*num_nodes-1] + solution[6*num_nodes-1] -
Tbstar) / Tbstar*100:.3f} %")
Solve time: 65.949 seconds
b'Algorithm stopped at a point that was converged, not to "desired" tolerances, but to "acceptable" tolerances (see the acceptable-... options).'
Objective value achieved: 5154.9859, as per the book it is 5152.0731, so the deviation is: 0.057 %
Individuals infected with resistant Tb = 1121.198, vs. 1123 from the book, hence deviation: -0.160 %
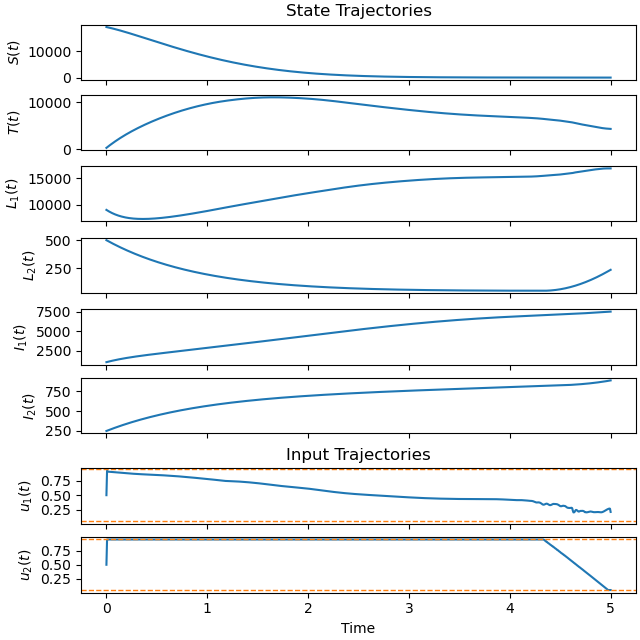
Plot the optimal state and input trajectories.
_ = prob.plot_trajectories(solution, show_bounds=True)
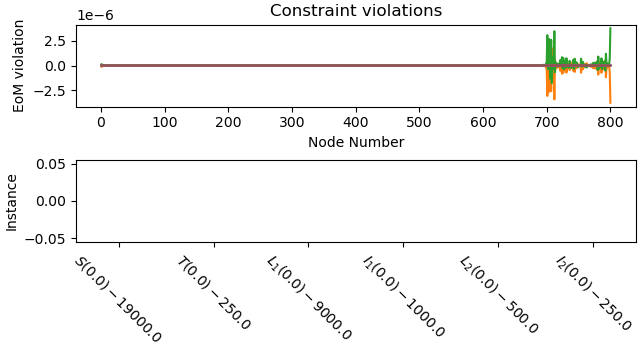
Plot the constraint violations.
_ = prob.plot_constraint_violations(solution)
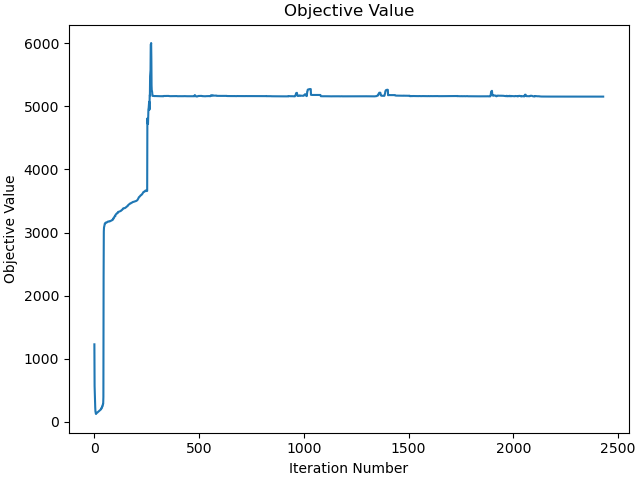
Plot the objective function as a function of optimizer iteration.
_ = prob.plot_objective_value()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 14.299 seconds)