Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Stiff Set of DAEs (betts-10-1)¶
This is example 10.1 from John T. Betts Practical Methods for Optimal Control Using NonlinearProgramming, 3rd edition, Chapter 10: Test Problems. More details are in section 4.11.7 of the book, where it says it was designed specifically to be hard to solve.
Notes:¶
The equations of motion do not seem to have any ‘physical’ meaning.
Only by relenting the bound on the inequality constraint from \(y^Ty \geq \textrm{function(time, parameters)}\) to \(y^Ty \geq \textrm{function(time, parameters)} - 0.01\), did the problem reach convergence.
seems very sensitive to the number of nodes used.
States
\(y_1, .., y_4\) : state variables as per the book
\(T\) : variable to keep track of the time.
Specifieds
\(u_1, u_2\) : control variables
import time
import numpy as np
import sympy as sm
import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
from opty.direct_collocation import Problem
from opty.utils import create_objective_function, MathJaxRepr
Equations of Motion¶
t = me.dynamicsymbols._t
y1, y2, y3, y4 = me.dynamicsymbols('y1 y2 y3 y4')
u1, u2 = me.dynamicsymbols('u1 u2')
As the time occurs explicitly in the equations of motion, and presently opty does not support that, a new state T(t) is introduced to keep track of time.
T = sm.symbols('T', cls=sm.Function)
Get the rhs of the algebraic inequality.
def p(t, a, b):
return sm.exp(-b*(t - a)**2)
terrain = (3.0*(p(T(t), 3, 12) + p(T(t), 6, 10) + p(T(t), 10, 6)) +
8.0*p(T(t), 15, 4) + 0.01)
Formulate the equations of motion as per the book.
eom = sm.Matrix([
-y1.diff(t) - 10*y1 + u1 + u2,
-y2.diff(t) - 2*y2 + u1 - 2*u2,
-y3.diff(t) - 3*y3 + 5*y4 + u1 - u2,
-y4.diff(t) + 5*y3 - 3*y4 + u1 + 3*u2,
y1**2 + y2**2 + y3**2 + y4**2 - terrain,
T(t).diff(t) - 1,
])
MathJaxRepr(eom)
Set up and Solve the Optimization Problem¶
t0, tf = 0.0, 20.0
num_nodes = 501
interval_value = (tf - t0) / (num_nodes - 1)
times = np.linspace(t0, tf, num_nodes)
state_symbols = (y1, y2, y3, y4, T(t))
specified_symbols = (u1, u2)
integration_method = 'backward euler'
Specify the objective function and form the gradient.
obj_func = sm.Integral(100.0*(y1**2 + y2**2 + y3**2 + y4**2)
+ 0.01*(u1**2 + u2**2), t)
obj, obj_grad = create_objective_function(
obj_func,
state_symbols,
specified_symbols,
tuple(),
num_nodes,
node_time_interval=interval_value,
integration_method=integration_method,
)
Specify the symbolic instance constraints, as per the example.
instance_constraints = (
T(t0) - t0,
y1.func(t0) - 2.0,
y2.func(t0) - 1.0,
y3.func(t0) - 2.0,
y4.func(t0) - 1.0,
y1.func(tf) - 2.0,
y2.func(tf) - 3.0,
y3.func(tf) - 1.0,
y4.func(tf) + 2.0,
)
Specify the equation of motion bounds. Here the left side of the interval is changed from 0.0 to -0.01 to get convergence.
eom_bounds = {4: (-0.01, np.inf)}
Create the optimization problem, set some options.
prob = Problem(
obj,
obj_grad,
eom,
state_symbols,
num_nodes,
interval_value,
instance_constraints=instance_constraints,
eom_bounds=eom_bounds,
integration_method=integration_method,
time_symbol=t,
)
prob.add_option('nlp_scaling_method', 'gradient-based')
prob.add_option('max_iter', 8000)
Give some rough estimates for the trajectories.
initial_guess = np.zeros(prob.num_free)
Solve the optimization problem.
start = time.time()
solution, info = prob.solve(initial_guess)
print(info['status_msg'])
print(f"Objective value achieved: {info['obj_val']:.4f}, as per the book ",
f"it is {2030.85609}, so the difference is: "
f"{(info['obj_val'] - 2030.85609)/2030.85609*100:.3f} % \n ")
end = time.time()
print(f'Total time needed: {end - start:.2f} seconds')
b'Algorithm stopped at a point that was converged, not to "desired" tolerances, but to "acceptable" tolerances (see the acceptable-... options).'
Objective value achieved: 2009.5722, as per the book it is 2030.85609, so the difference is: -1.048 %
Total time needed: 146.06 seconds
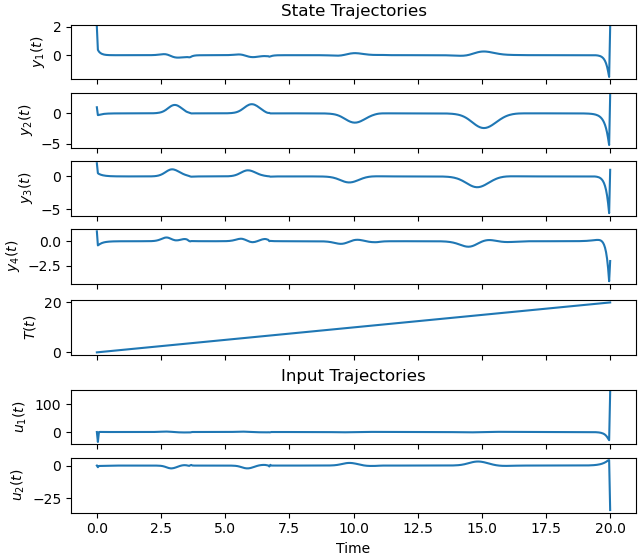
Plot the optimal state and input trajectories.
_ = prob.plot_trajectories(solution)
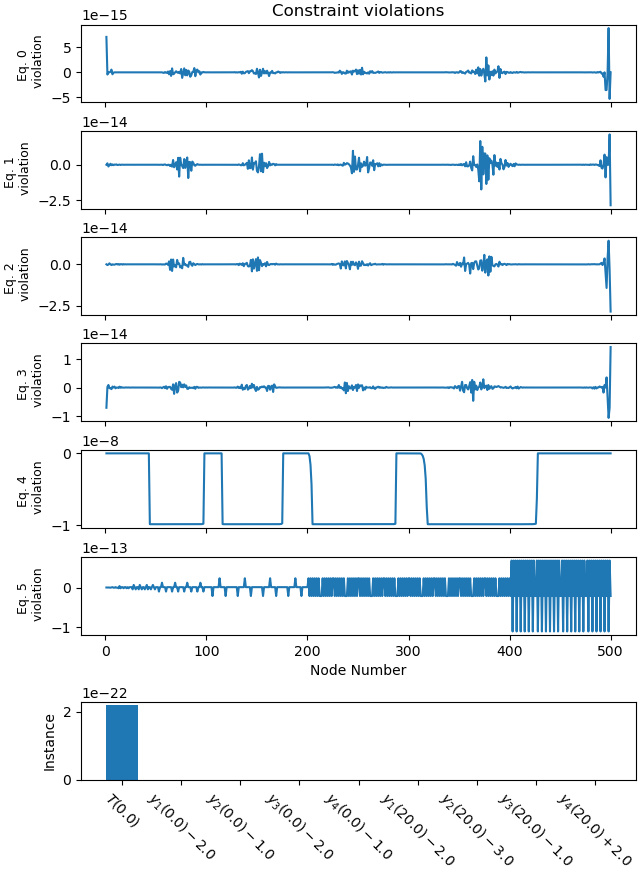
Plot the constraint violations.
_ =prob.plot_constraint_violations(solution, subplots=True)
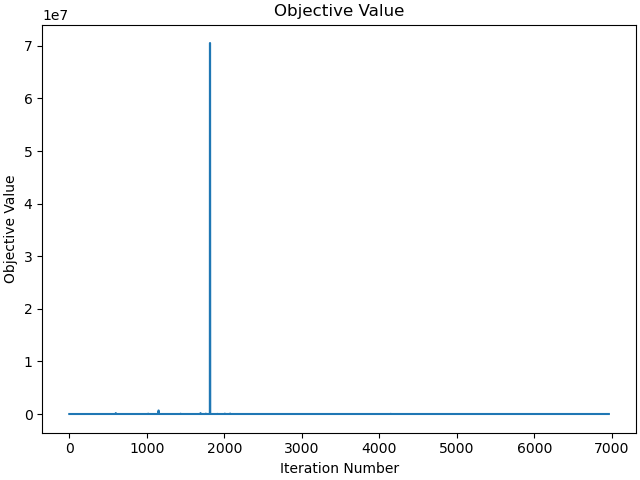
Plot the objective function as a function of optimizer iteration.
_ = prob.plot_objective_value()
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 37.207 seconds)