Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
3D Drone with Propellers¶
Objectives¶
Show how opty can optimize unknown trajectories (here: the torques on the propellers of a drone) and known parameters (here: the radius of the propellers) simultaneously and also it optimizes the speed.
Show how sometimes one gets better results with an iterative approach.
Show how different objective functions, with the same goal - a balance between speed and energy consumption - can affect the results.
Description¶
A drone is modeled as a rigid body in 3D space, with four propellers attached to it. The drone’s body is represented as a solid ball, and the propellers are modeled as solid discs. To create lift, two propellers must rotate ‘positively’, two ‘negatively’, else the drone will rotate. Also the radius of the propeller is optimized.
The objective function to be minimized is \(\int_0^{t_{\text{final}}} (T_1^2 + T_2^2 + T_3^2 + T_4^2) \, dt + \textrm{weight} \cdot t_{\text{final}}\) , where \(T_i\) is the torque applied to propeller i, and \(t_{\text{final}}\) is the final time of the trajectory, it is variable, its value determined by opty.
Notes¶
Initially this objective function was used: \(t_{\text{final}}^7 \cdot \int_0^{t_{\text{final}}} (T_1^2 + T_2^2 + T_3^2 + T_4^2) \, dt\) It converged easily, but the duration of the flight varied from 6.8 sec to 9.4 sec, identical initial conditions. Apparently high powers of the variable time interval are to be avoided.
This is merely a somewhat more complex example of this one: https://opty.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/intermediate/plot_drone.html#sphx-glr-examples-intermediate-plot-drone-py
The relationships regarding friction, lifting power of the propellers, etc., are arbitrary.
States
\(x, y, z\) : Position of the drone body’s mass center in 3D space.
\(q_1, q_2, q_3\) : Angles of rotation of the drone body in 3D space.
\(u_x, u_y, u_z\) : Linear velocities of the drone body in 3D space.
\(u_1, u_2, u_3\) : Angular velocities of the drone body in 3D space.
\(q_{p1}, q_{p2}, q_{p3}, q_{p4}\) : rotation angles of the propellers.
\(u_{p1}, u_{p2}, u_{p3}, u_{p4}\) : Angular velocity of the propellers.
Control Inputs
\(T_1, T_2, T_3, T_4\) : Torques applied to the propellers.
Parameters
\(m_D, m_M, m_P\) : Masses of the drone body, motors, and propellers.
\(g\) : Gravitational acceleration.
\(a\) : Distance of the motors from the drone’s mass center.
\(r_b, r_M, r_P\) : Radii of the drone body, motors, and propellers.
\(l_1\) : Distance of the propellers from the motors.
\(\text{reibung}\) : Friction coefficient for the drone body.
\(\text{reibungP}\) : Friction coefficient for the propellers.
\(\text{x_m, y_m, z_m}\) : Coordinates of an intermediate stopping point.
\(\textrm{weight}\) : Relative importance of the speed.
import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
import numpy as np
import sympy as sm
from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline
from opty.direct_collocation import Problem
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
Kane’s Equations of Motion¶
# inertial frame, frame of the drone body
N, Ab = sm.symbols('N Ab', cls=me.ReferenceFrame)
# frame of the propellers.
Ap1, Ap2, Ap3, Ap4 = sm.symbols('Ap1 Ap2 Ap3 Ap4', cls=me.ReferenceFrame)
t = me.dynamicsymbols._t
# origin, mass center of the drone, of the motors P1...P4
O, DmcD, P1, P2, P3, P4 = sm.symbols('O DmcD P1 P2 P3 P4', cls=me.Point)
# mass centers of the propellers
Pp1, Pp2, Pp3, Pp4 = sm.symbols('Pp1 Pp2 Pp3 Pp4', cls=me.Point)
O.set_vel(N, 0)
# position of the mass center of the drone
x, y, z = me.dynamicsymbols('x y z')
ux, uy, uz = me.dynamicsymbols('u_x, u_y, u_z')
# angle of rotation of the drone wrt N
q1, q2, q3 = me.dynamicsymbols('q_1, q_2, q_3')
u1, u2, u3 = me.dynamicsymbols('u_1, u_2, u_3')
# angle of rotation of the propellers wrt Ab
qp1, qp2, qp3, qp4 = me.dynamicsymbols('q_p1, q_p2, q_p3, q_p4')
up1, up2, up3, up4 = me.dynamicsymbols('u_p1, u_p2, u_p3, u_p4')
# torques applied to the propellers, control input
T1, T2, T3, T4 = me.dynamicsymbols('T_1, T_2, T_3, T_4')
# mass of body of ther drone, mass of the motors, mass of propellers per unit
# radius of it , gravity, distance of the motors from the mass center,
# friction coefficient
mD, mM, mP, g, a, reibung = sm.symbols('m_D,m_M, m_P, g, a, reibung')
# radius of the body, radius of the motors, radius of the propellers,
# location of the propellers 'above' the drone
rb, rM, rP, l1 = sm.symbols('r_b r_M r_P l_1')
# Location of the intermediate stopping point.
xm, ym, zm = sm.symbols('xm ym zm')
# friction coefficient of the propellers
reibungP = sm.symbols('reibungP')
Ab.orient_body_fixed(N, (q1, q2, q3), 'XYZ')
rot = Ab.ang_vel_in(N) # needed for the kinematic equations
Ab.set_ang_vel(N, u1 * Ab.x + u2*Ab.y + u3*Ab.z)
rot1 = Ab.ang_vel_in(N) # needed for the kinematic equations
# orientation of the propellers
Ap1.orient_axis(Ab, qp1, Ab.z)
Ap1.set_ang_vel(Ab, up1 * Ab.z)
Ap2.orient_axis(Ab, qp2, Ab.z)
Ap2.set_ang_vel(Ab, up2 * Ab.z)
Ap3.orient_axis(Ab, qp3, Ab.z)
Ap3.set_ang_vel(Ab, up3 * Ab.z)
Ap4.orient_axis(Ab, qp4, Ab.z)
Ap4.set_ang_vel(Ab, up4 * Ab.z)
# position of the mass center of the drone
DmcD.set_pos(O, x*N.x + y*N.y + z*N.z)
DmcD.set_vel(N, ux*N.x + uy*N.y + uz*N.z)
# position of the motors
P1.set_pos(DmcD, a * Ab.x)
P2.set_pos(DmcD, -a * Ab.x)
P3.set_pos(DmcD, a * Ab.y)
P4.set_pos(DmcD, -a * Ab.y)
P1.v2pt_theory(DmcD, N, Ab)
P2.v2pt_theory(DmcD, N, Ab)
P3.v2pt_theory(DmcD, N, Ab)
P4.v2pt_theory(DmcD, N, Ab)
# position of the propellers
Pp1.set_pos(P1, l1 * Ab.z)
Pp2.set_pos(P2, l1 * Ab.z)
Pp3.set_pos(P3, l1 * Ab.z)
Pp4.set_pos(P4, l1 * Ab.z)
Pp1.v2pt_theory(P1, N, Ab)
Pp2.v2pt_theory(P2, N, Ab)
Pp3.v2pt_theory(P3, N, Ab)
Pp4.v2pt_theory(P4, N, Ab)
# Create the bodies
# drone body and motors are modelled as solid balls of of radius rb, rM and
# masses mD, mM
# the propellers are modelled as solid disks of radius rP and mass mP
iXXd = 2 / 5 * mD * rb**2
iYYd = iXXd
iZZd = iXXd
inertiaD = (me.inertia(Ab, iXXd, iYYd, iZZd))
DmcDa = me.RigidBody('DmcDa', DmcD, Ab, mD, (inertiaD, DmcD))
iXXm = 2 / 5 * mM * rM**2
iYYm = iXXm
iZZm = iXXm
inertiaM = (me.inertia(Ab, iXXm, iYYm, iZZm))
P1a = me.RigidBody('P1a', P1, Ab, mM, (inertiaM, P1))
P2a = me.RigidBody('P2a', P2, Ab, mM, (inertiaM, P2))
P3a = me.RigidBody('P3a', P3, Ab, mM, (inertiaM, P3))
P4a = me.RigidBody('P4a', P4, Ab, mM, (inertiaM, P4))
iXXp = 1./4. * (mP * rP) * rP**2
iYYp = iXXp
iZZp = 1./2. * (mP * rP) * rP**2
inertiaP1 = (me.inertia(Ap1, iXXp, iYYp, iZZp))
inertiaP2 = (me.inertia(Ap2, iXXp, iYYp, iZZp))
inertiaP3 = (me.inertia(Ap3, iXXp, iYYp, iZZp))
inertiaP4 = (me.inertia(Ap4, iXXp, iYYp, iZZp))
Pp1a = me.RigidBody('Pp1a', Pp1, Ap1, mP, (inertiaP1, Pp1))
Pp2a = me.RigidBody('Pp2a', Pp2, Ap2, mP, (inertiaP2, Pp2))
Pp3a = me.RigidBody('Pp3a', Pp3, Ap3, mP, (inertiaP3, Pp3))
Pp4a = me.RigidBody('Pp4a', Pp4, Ap4, mP, (inertiaP4, Pp4))
BODY = [DmcDa, P1a, P2a, P3a, P4a, Pp1a, Pp2a, Pp3a, Pp4a]
Forces
It is assumed that the frictional forces are proportionmal to the velocity of the drone squared, and diminish with height. The exponents used for the radius of the propellers, rD, for the fritction and for the lift are arbitrary.
FL = [
# drive the propellers. the control variables.
(Ap1, T1 * Ab.z - reibungP * rP**(2/3) * up1 * Ab.z),
(Ap2, T2 * Ab.z - reibungP * rP**(2/3) * up2 * Ab.z),
(Ap3, T3 * Ab.z - reibungP * rP**(2/3) * up3 * Ab.z),
(Ap4, T4 * Ab.z - reibungP * rP**(2/3) * up4 * Ab.z),
# moment of the propellers onto the drone
(Ab, -(T1 + T2 + T3 + T4) * Ab.z),
(DmcD, -mD*g*N.z - reibung * DmcD.vel(N).magnitude()*DmcD.vel(N) /
(1 + z**2)),
(P1, -mM*g*N.z - reibung * P1.vel(N).magnitude()*P1.vel(N) / (1 + z**2)),
(P2, -mM*g*N.z - reibung * P2.vel(N).magnitude()*P2.vel(N) / (1 + z**2)),
(P3, -mM*g*N.z - reibung * P3.vel(N).magnitude()*P3.vel(N) / (1 + z**2)),
(P4, -mM*g*N.z - reibung * P4.vel(N).magnitude()*P4.vel(N) / (1 + z**2)),
# propellers must run in different directions
# otherwise the drone will rotate.
(Pp1, -mP*g*N.z - reibung * Pp1.vel(N).magnitude()*Pp1.vel(N) /
(1 + z**2) + rP**2 * up1 * Ap1.z),
(Pp2, -mP*g*N.z - reibung * Pp2.vel(N).magnitude()*Pp2.vel(N) /
(1 + z**2) - rP**2 * up2 * Ap2.z),
(Pp3, -mP*g*N.z - reibung * Pp3.vel(N).magnitude()*Pp3.vel(N) /
(1 + z**2) + rP**2 * up3 * Ap3.z),
(Pp4, -mP*g*N.z - reibung * Pp4.vel(N).magnitude()*Pp4.vel(N) /
(1 + z**2) - rP**2 * up4 * Ap4.z),
]
kd = sm.Matrix([
ux - x.diff(t), uy - y.diff(t), uz - z.diff(t),
*[(rot-rot1).dot(uv) for uv in N],
up1 - qp1.diff(t), up2 - qp2.diff(t), up3 - qp3.diff(t),
up4 - qp4.diff(t),
])
q_ind = [x, y, z, q1, q2, q3, qp1, qp2, qp3, qp4]
u_ind = [ux, uy, uz, u1, u2, u3, up1, up2, up3, up4]
# Create the KanesMethod object
KM = me.KanesMethod(
N,
q_ind=q_ind,
u_ind=u_ind,
kd_eqs=kd,
)
fr, frstar = KM.kanes_equations(BODY, FL)
EOM = kd.col_join(fr + frstar)
print('EOM shape', EOM.shape, '\n')
print('EOM DS', me.find_dynamicsymbols(EOM), '\n')
print('EOM FS', EOM.free_symbols, '\n')
print(f'EOMs contain {sm.count_ops(EOM):,} operations')
qL = [wert for wert in KM.q] + [wert for wert in KM.u]
print('sequence of states:', qL)
EOM shape (20, 1)
EOM DS {u_1(t), Derivative(q_3(t), t), Derivative(q_p4(t), t), Derivative(u_2(t), t), Derivative(u_y(t), t), u_p1(t), x(t), q_p1(t), Derivative(q_p3(t), t), u_y(t), u_2(t), u_z(t), z(t), Derivative(u_p2(t), t), Derivative(u_1(t), t), Derivative(u_3(t), t), T_1(t), Derivative(u_x(t), t), T_2(t), u_p3(t), q_3(t), Derivative(q_p1(t), t), u_p4(t), Derivative(x(t), t), q_1(t), q_p2(t), Derivative(u_p4(t), t), T_4(t), Derivative(q_1(t), t), Derivative(y(t), t), y(t), Derivative(q_p2(t), t), u_x(t), Derivative(u_z(t), t), Derivative(u_p3(t), t), q_p3(t), u_3(t), Derivative(z(t), t), q_2(t), Derivative(u_p1(t), t), q_p4(t), u_p2(t), Derivative(q_2(t), t), T_3(t)}
EOM FS {a, m_M, r_P, reibung, t, l_1, m_D, m_P, r_M, g, reibungP, r_b}
EOMs contain 48,470 operations
sequence of states: [x(t), y(t), z(t), q_1(t), q_2(t), q_3(t), q_p1(t), q_p2(t), q_p3(t), q_p4(t), u_x(t), u_y(t), u_z(t), u_1(t), u_2(t), u_3(t), u_p1(t), u_p2(t), u_p3(t), u_p4(t)]
Set Up the Optimization Problem and Solve It¶
state_symbols = qL
laenge = len(state_symbols)
constant_symbols = tuple((mD, mM, mP, g, a, reibung, rb, rM, l1))
specified_symbols = ((T1, T2, T3, T4))
unknown_symbols = [rP]
# Specify the known system parameters.
par_map = {}
par_map[mD] = 5.0 # Mass of the drone body
par_map[mM] = 0.5 # Mass of the motors
par_map[mP] = 0.1 # Mass of the propellers
par_map[g] = 9.81 # Acceleration due to gravity
par_map[a] = 3.0 # Distance of the mass center of the drone from P_i
par_map[reibung] = 0.1 # Friction coefficient.
par_map[reibungP] = 0.25 # Friction coefficient of the propellers
par_map[rb] = 2.0 # Radius of the body
par_map[rM] = 0.5 # Radius of the motors
par_map[l1] = 0.5 # Distance of the propellers from the mass center
par_map[xm] = 50.0 # x-coordinate of the goal point
par_map[ym] = 50.0 # y-coordinate of the goal point
par_map[zm] = 75.0 # z-coordinate of the goal point
num_nodes = 100 # The number of nodes
h = sm.symbols('h', real=True)
interval_value = h
t0, t_int, tf = 0.0, num_nodes // 2 * h, (num_nodes - 1) * h
weight = 1.e6
def obj(free):
summe = (np.sum(free[20 * num_nodes: 24 * num_nodes]**2) * free[-1] +
weight * free[-1])
return summe
def obj_grad(free):
"""Gradient of the objective function."""
grad = np.zeros_like(free)
grad[20 * num_nodes: 24 * num_nodes] = (2 * free[20 * num_nodes: 24 *
num_nodes] * free[-1])
grad[-1] = np.sum(free[20 * num_nodes: 24 * num_nodes]**2) + weight
return grad
initial_state_constraints = {
x: 0.0,
y: 0.0,
z: 0.0,
q1: 0.0,
q2: 0.0,
q3: 0.0,
qp1: 0.0,
qp2: 0.0,
qp3: 0.0,
qp4: 0.0,
ux: 0.0,
uy: 0.0,
uz: 0.0,
u1: 0.0,
u2: 0.0,
u3: 0.0,
up1: 0.0,
up2: 0.0,
up3: 0.0,
up4: 0.0,
}
intermediate_state_constraints = {
x: par_map[xm],
y: par_map[ym],
z: par_map[zm],
q1: 0.0,
q2: 0.0,
q3: 0.0,
ux: 0.0, # Value has no meaning, will be set during iteratio
uy: 0.0, # Value has no meaning, will be set during iteration
uz: 0.0, # Value has no meaning, will be set during iteration
u1: 0.0,
u2: 0.0,
u3: 0.0
}
final_state_constraints = {
x: 100.0,
y: 100.0,
z: 100.0,
q1: 0.0,
q2: 0.0,
q3: 0.0,
ux: 0.0, # Value has no meaning, will be set during iteration
uy: 0.0, # Value has no meaning, will be set during iteration
uz: 0.0, # Value has no meaning, will be set during iteration
u1: 0.0,
u2: 0.0,
u3: 0.0,
}
staerke = 100.0 # The maximum strength of the control input
teiler = 3.0
bounds = {
h: (0.0, 0.5), # Bounding h > 0 avoids problems with negative time.
T1: (-staerke, staerke),
T2: (-staerke, staerke),
T3: (-staerke, staerke),
T4: (-staerke, staerke),
x: (0., 110),
y: (0., 110),
z: (0., 110),
# the drone must not rotate too much
q1: (-np.pi / teiler, np.pi / teiler),
q2: (-np.pi / teiler, np.pi / teiler),
rP: (0.5, 5.0),
}
instance_constraints = (
*tuple(xi.subs({t: t0}) - xi_val for xi, xi_val in
initial_state_constraints.items()),
*tuple(xi.subs({t: t_int}) - xi_val for xi, xi_val in
intermediate_state_constraints.items()),
*tuple(xi.subs({t: tf}) - xi_val for xi, xi_val in
final_state_constraints.items()),
)
iterationen = 5
teilen = iterationen / 2.5
approximation = 2.5001
for i in range(iterationen):
# for some reason, the intermediate / final states ux = uy = uz = 0 give
# problems. Hence iteration towards them. Approximation = 2.5, that is
# ux = uy = uz = 0 at the end of the iteration will created problems.
# Trying to go there in one step (no iteration) will give a result, which
# clearly is not optimal.
final_state_constraints[ux] = approximation - (i+1) / teilen
final_state_constraints[uy] = approximation - (i+1) / teilen
final_state_constraints[uz] = approximation - (i+1) / teilen
intermediate_state_constraints[ux] = approximation - (i+1) / teilen
intermediate_state_constraints[uy] = approximation - (i+1) / teilen
intermediate_state_constraints[uz] = approximation - (i+1) / teilen
instance_constraints = (
*tuple(xi.subs({t: t0}) - xi_val for xi, xi_val in
initial_state_constraints.items()),
*tuple(xi.subs({t: t_int}) - xi_val for xi, xi_val in
intermediate_state_constraints.items()),
*tuple(xi.subs({t: tf}) - xi_val for xi, xi_val in
final_state_constraints.items()),
)
prob = Problem(
obj,
obj_grad,
EOM,
state_symbols,
num_nodes,
interval_value,
known_parameter_map=par_map,
instance_constraints=instance_constraints,
bounds=bounds,
)
prob.add_option('max_iter', 3000) # default is 3000
if i == 0:
initial_guess = np.ones(prob.num_free)
# Find the optimal solution.
solution, info = prob.solve(initial_guess)
print(f'{i+1} - th iteration')
print('message from optimizer:', info['status_msg'])
print('Iterations needed', len(prob.obj_value))
print(f"objective value {info['obj_val']:.3e}")
print(f'radius of propellers {solution[-2]:.3f} \n')
initial_guess = solution
1 - th iteration
message from optimizer: b'Algorithm terminated successfully at a locally optimal point, satisfying the convergence tolerances (can be specified by options).'
Iterations needed 127
objective value 7.473e+04
radius of propellers 1.352
2 - th iteration
message from optimizer: b'Algorithm stopped at a point that was converged, not to "desired" tolerances, but to "acceptable" tolerances (see the acceptable-... options).'
Iterations needed 135
objective value 7.540e+04
radius of propellers 1.355
3 - th iteration
message from optimizer: b'Algorithm stopped at a point that was converged, not to "desired" tolerances, but to "acceptable" tolerances (see the acceptable-... options).'
Iterations needed 210
objective value 7.607e+04
radius of propellers 1.358
4 - th iteration
message from optimizer: b'Algorithm stopped at a point that was converged, not to "desired" tolerances, but to "acceptable" tolerances (see the acceptable-... options).'
Iterations needed 233
objective value 7.674e+04
radius of propellers 1.361
5 - th iteration
message from optimizer: b'Algorithm stopped at a point that was converged, not to "desired" tolerances, but to "acceptable" tolerances (see the acceptable-... options).'
Iterations needed 75
objective value 7.742e+04
radius of propellers 1.364
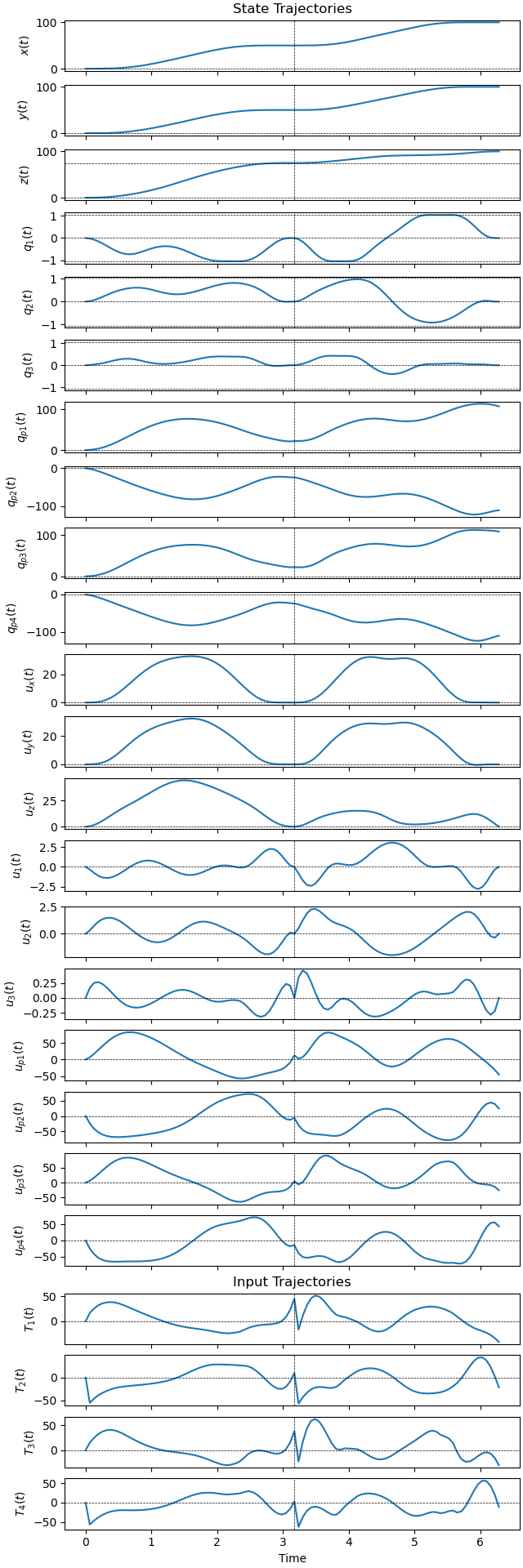
Plot the results.
ax = prob.plot_trajectories(solution)
center = solution[-1] * (num_nodes // 2)
for i in range(len(ax)):
ax[i].axvline(center, color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
ax[i].axhline(0.0, color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
ax[2].axhline(par_map[zm], color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
limit = np.pi / teiler
for i in range(3, 6):
ax[i].axhline(-limit, color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
_ = ax[i].axhline(limit, color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
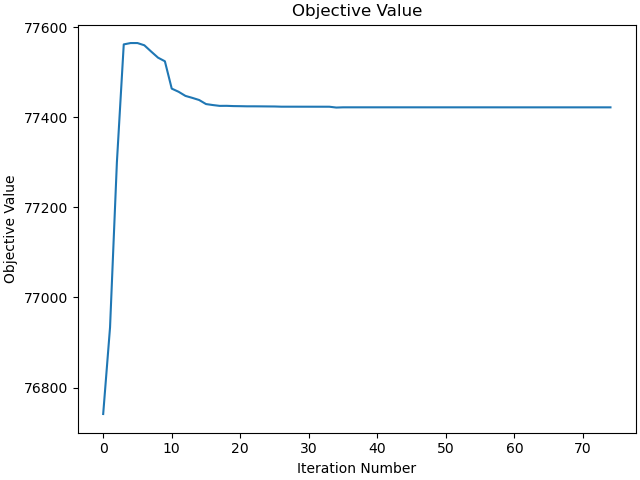
Plot the objective values.
_ = prob.plot_objective_value()
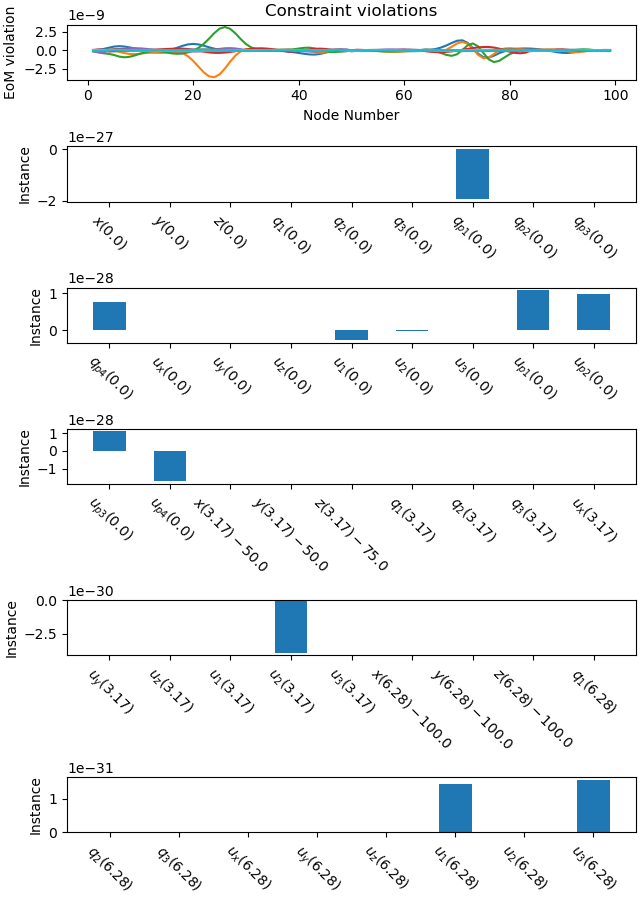
Plot the constraint violations.
_ = prob.plot_constraint_violations(solution)
Animation¶
fps = 10
# trace the paths of the drone body and of the propellers
traceD = []
state_vals, input_vals, prop_radius, h_val = prob.parse_free(solution)
tf = h_val * (num_nodes - 1)
t_arr = np.linspace(t0, tf, num_nodes)
state_sol = CubicSpline(t_arr, state_vals.T)
input_sol = CubicSpline(t_arr, input_vals.T)
qL = [*state_symbols, *specified_symbols]
par_map[a] = 15. # I change this for better visibility
pL, pL_vals = [*constant_symbols], [par_map[const]
for const in constant_symbols]
# define final points of the force arrows
# the forces of the propellers on the drone, will be calculated below
f1, f2, f3, f4 = sm.symbols('f1 f2 f3 f4')
Ff1, Ff2, Ff3, Ff4 = sm.symbols('Ff1, Ff2, Ff3, Ff4', cls=me.Point)
Ff1.set_pos(P1, f1 * Ab.z)
Ff2.set_pos(P2, f2 * Ab.z)
Ff3.set_pos(P3, f3 * Ab.z)
Ff4.set_pos(P4, f4 * Ab.z)
head = me.Point('head')
head.set_pos(DmcD, 15.0 * par_map[l1] * Ab.z)
coordinates = DmcD.pos_from(O).to_matrix(N)
for point in [P1, P2, P3, P4, Ff1, Ff2, Ff3, Ff4, head]:
coordinates = coordinates.row_join(point.pos_from(O).to_matrix(N))
coords_lam = sm.lambdify(qL + pL + [f1, f2, f3, f4], coordinates, cse=True)
# to keep the order of the states in the animation
idx = []
for ort in initial_state_constraints.keys():
idx.append(qL.index(ort))
# needed to give the picture the right size
xmin, xmax = (np.min(state_vals[idx[0], :]) -
par_map[a], np.max(state_vals[idx[0], :]) + par_map[a])
ymin, ymax = (np.min(state_vals[idx[1], :]) -
par_map[a], np.max(state_vals[idx[1], :]) + par_map[a])
zmin, zmax = (np.min(state_vals[idx[2], :]) -
par_map[a], np.max(state_vals[idx[2], :]) + par_map[a])
def plot_3d_plane(x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max):
# Create a meshgrid for x and y values
x = np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 100)
y = np.linspace(y_min, y_max, 100)
x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
# Z values are set to 0 for the plane
z = np.zeros_like(x)
# Plot the 3D plane
ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, alpha=0.1, rstride=100, cstride=100, color='c')
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.set_xlim(xmin - 1., xmax + 1.)
ax.set_ylim(ymin - 1., ymax + 1.)
ax.set_zlim(zmin - 1., zmax + 1.)
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_zlabel('Z-axis')
ebene = plot_3d_plane(xmin - 1., xmax + 1., ymin - 1., ymax + 1.)
# Drone body, dorne 'head
line1, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='red', marker='o', markersize=10)
line1a, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='blue', marker='o', markersize=10)
# Propellers
line2, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='blue', marker='o', markersize=5)
line3, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='magenta', marker='o', markersize=5)
line4, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='orange', marker='o', markersize=5)
line5, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', marker='o', markersize=5)
# Connecting lines between propellers
line6, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=0.5, markersize=1)
line7, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=0.5, markersize=1)
# line conneting drone body to drone head
line7a, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=1.0, markersize=0)
# Trace line for the drone body
line8, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='red', lw=0.5, markersize=1)
# Quiver arrows for the forces
quiver1 = ax.quiver([], [], [], [], [], [], color='r')
quiver2 = ax.quiver([], [], [], [], [], [], color='r')
quiver3 = ax.quiver([], [], [], [], [], [], color='r')
quiver4 = ax.quiver([], [], [], [], [], [], color='r')
# Start, intermediate, and final points
ax.plot(initial_state_constraints[x], initial_state_constraints[y],
initial_state_constraints[z], marker='o', markersize=5, color='red')
ax.plot(intermediate_state_constraints[x], intermediate_state_constraints[y],
intermediate_state_constraints[z], marker='o', markersize=5,
color='blue')
ax.plot(final_state_constraints[x], final_state_constraints[y],
final_state_constraints[z], marker='o', markersize=5, color='green')
# Function to update the plot for each animation frame
def update(t):
global quiver1, quiver2, quiver3, quiver4
message = (f'Running time {t:.2f} sec \n The green arrows are the forces '
f'\n Optimal radius of the propellers is {solution[-2]:.3f}')
ax.set_title(message, fontsize=15)
# scaling factor for the forces, to make them look 'right'.
skala = 2.5
f11 = prop_radius[0]**2 * state_sol(t)[idx[-4]] / skala
f21 = -prop_radius[0]**2 * state_sol(t)[idx[-3]] / skala
f31 = prop_radius[0]**2 * state_sol(t)[idx[-2]] / skala
f41 = -prop_radius[0]**2 * state_sol(t)[idx[-1]] / skala
coords = coords_lam(*state_sol(t), *input_sol(t), *pL_vals, f11, f21,
f31, f41)
line1.set_data([coords[0, 0]], [coords[1, 0]])
line1.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 0]])
line1a.set_data([coords[0, 9]], [coords[1, 9]])
line1a.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 9]])
line2.set_data([coords[0, 1]], [coords[1, 1]])
line2.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 1]])
line3.set_data([coords[0, 2]], [coords[1, 2]])
line3.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 2]])
line4.set_data([coords[0, 3]], [coords[1, 3]])
line4.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 3]])
line5.set_data([coords[0, 4]], [coords[1, 4]])
line5.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 4]])
line6.set_data([coords[0, 1], coords[0, 2]], [coords[1, 1], coords[1, 2]])
line7.set_data([coords[0, 3], coords[0, 4]], [coords[1, 3], coords[1, 4]])
line7.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 3], coords[2, 4]])
line7a.set_data([coords[0, 0], coords[0, 9]], [coords[1, 0], coords[1, 9]])
line7a.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 0], coords[2, 9]])
line6.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 1], coords[2, 2]])
quiver1.remove()
quiver2.remove()
quiver3.remove()
quiver4.remove()
quiver1 = ax.quiver(coords[0, 1], coords[1, 1], coords[2, 1],
coords[0, 5] - coords[0, 1], coords[1, 5] -
coords[1, 1], coords[2, 5] - coords[2, 1], color='g')
quiver2 = ax.quiver(coords[0, 2], coords[1, 2], coords[2, 2],
coords[0, 6] - coords[0, 2], coords[1, 6] -
coords[1, 2], coords[2, 6] - coords[2, 2], color='g')
quiver3 = ax.quiver(coords[0, 3], coords[1, 3], coords[2, 3],
coords[0, 7] - coords[0, 3], coords[1, 7] -
coords[1, 3], coords[2, 7] - coords[2, 3], color='g')
quiver4 = ax.quiver(coords[0, 4], coords[1, 4], coords[2, 4],
coords[0, 8] - coords[0, 4], coords[1, 8] -
coords[1, 4], coords[2, 8] - coords[2, 4], color='g')
traceD.append([coords[0, 0], coords[1, 0], coords[2, 0]])
line8.set_data(np.array(traceD)[:, 0:2].T)
line8.set_3d_properties(np.array(traceD)[:, 2])
# Create the animation
animation = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=np.arange(t0, tf, 1 / fps),
interval=1000 / fps)
plt.show()