Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Explorer Anomaly¶
Objectives¶
Show how to use generate_ode_function as a fast alternative for lambdify
Show how to use PyDy Visualization to create a 3D animation
Description¶
It is known, that for a rigid body the rotation around the axes of maximum or minimum moment of inertia is stable. Explorer1 showed, that the rotation around the axis of minimum moment of inertia may be unstable if the body is not rigid.
Many more details may be found here:
https://nescacademy.nasa.gov/video/cfbf4765ea984d05b2b5df46d2939ee11d which was also the inspiration for this example.
Here the explorer is modeled as a rigid body, a hollow tube. Four antennas are attached to the explorer via spherical joints. The antennas are modeled as thin rods. Their attachment points are located on a circumference near the center of gravity of the explorer, evenly spaced. Their neutral direction is normal to the surface of the explorer at the points of attachment. When they are deflected from their neutral position, a restoring torque acts on them, proportional to the deflection angle and a damping torque, proportional to the angular velocity, with constants \(k_\textrm{{torque}}\) and \(\mu_\textrm{{torque}}\). The opposite torque acts on the explorer.
As this takes place in outer space no gravity is present.
Notes¶
The dimensions and the masses of the explorer and the antennas are, as well as the constants \(k_\textrm{{torque}}\) and \(\mu_\textrm{{torque}}\) are courtesy Dr. David Levinson via Dr. Carlos Roithmayr.
The equations of motion are derived using Kane’s method.
As there is dampening, the total energy of the system decreases.
As there are no external forces or torques, the angular momentum of the system must be constant.
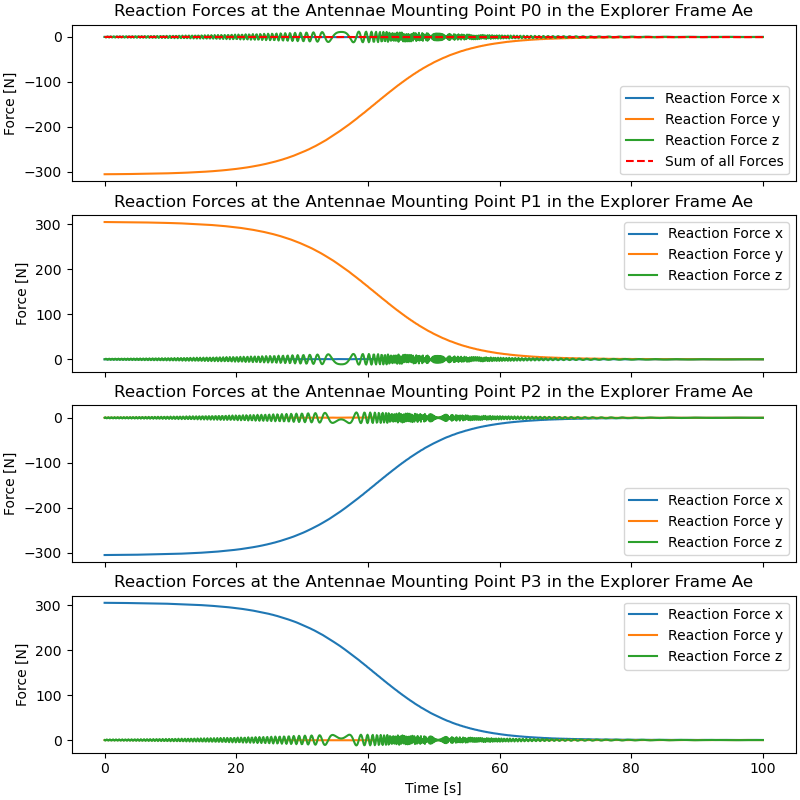
For the determination of the reaction forces at the connection points the accelerations are needed. As generate_ode_function needs C - contiguous arrays, a bit of care has to be taken there.
With PyDy Visualisation the axis of a cylinder is always in the Y direction. If this was not considered when setting up the system, it must be corrected when defining the visualization frames - as it is done here.
States
\(x, y, z\) : Position of the center of gravity of the explorer in the inertial frame
\(u_x, u_y, u_z\) : Velocity of the center of gravity of the explorer in the inertial frame
\(q_{ex}, q_{ey}, q_{ez}\) : Orientation of the body fixed frame of the explorer
\(u_{ex}, u_{ey}, u_{ez}\) : Angular velocity of the body fixed frame of the explorer
\(q_{0x}, q_{0z}\) : Orientation of the body fixed frame of antenna 0
\(u_{0x}, u_{0z}\) : Angular velocity of the body fixed frame of antenna 0
\(q_{1x}, q_{1z}\) : Orientation of the body fixed frame of antenna 1
\(u_{1x}, u_{1z}\) : Angular velocity of the body fixed frame of antenna 1
\(q_{2y}, q_{2z}\) : Orientation of the body fixed frame of antenna 2
\(u_{2y}, u_{2z}\) : Angular velocity of the body fixed frame of antenna 2
\(q_{3y}, q_{3z}\) : Orientation of the body fixed frame of antenna 3
\(u_{3y}, u_{3z}\) : Angular velocity of the body fixed frame of antenna 3
Parameters
\(m_e\) : Mass of the explorer
\(m_a\) : Mass of each antenna
\(r_{ei}\) : Inner radius of the explorer
\(r_{eo}\) : Outer radius of the explorer
\(L_e\) : Length of the explorer
\(L_a\) : Length of each antenna
\(\textrm{dist}\) : Distance of the attachment points of the antennas from the center of gravity of the explorer in radial direction
\(\textrm{shift}\) : Location of the attachment points of the antennas in the axial direction from the center of gravity of the explorer
\(k_\textrm{{torque}}\) : Spring constant
\(\mu_\textrm{{torque}}\) : Damping constant
import numpy as np
import sympy as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
from scipy.integrate import solve_ivp
from scipy.optimize import root
from scipy.interpolate import CubicSpline
from pydy.codegen.ode_function_generators import generate_ode_function
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D # noqa: F401
from matplotlib import animation
Equations of Motion, Kane’s Method¶
N, Ae, Aa0, Aa1, Aa2, Aa3 = sm.symbols('N Ae Aa0 Aa1 Aa2 Aa3',
cls=me.ReferenceFrame)
O = me.Point('O')
O.set_vel(N, 0)
t = me.dynamicsymbols._t
# where the antennae attach to the explorer
P0, P1, P2, P3 = sm.symbols('P0 P1 P2 P3', cls=me.Point)
# Mass centers of the explorer and antennae
Aoe, Aoa0, Aoa1, Aoa2, Aoa3 = sm.symbols('Aoe Aoa0 Aoa1 Aoa2 Aoa3',
cls=me.Point)
# Coordinates of the mass center of the explorer
x, y, z, ux, uy, uz = me.dynamicsymbols('x, y, z, ux, uy, uz')
# Coordinates of body fixed frame of the explorer
qex, qey, qez = me.dynamicsymbols('qex, qey, qez')
uex, uey, uez = me.dynamicsymbols('uex, uey, uez')
# Coordinates of the body fixed frames of the antennae
q0x, q0z, u0x, u0z = me.dynamicsymbols('q0x, q0z, u0x, u0z')
q1x, q1z, u1x, u1z = me.dynamicsymbols('q1x, q1z, u1x, u1z')
q2y, q2z, u2y, u2z = me.dynamicsymbols('q2y, q2z, u2y, u2z')
q3y, q3z, u3y, u3z = me.dynamicsymbols('q3y, q3z, u3y, u3z')
aux0x, aux0y, aux0z, f0x, f0y, f0z = me.dynamicsymbols(
'aux0x, aux0y, aux0z, f0x, f0y, f0z')
aux1x, aux1y, aux1z, f1x, f1y, f1z = me.dynamicsymbols(
'aux1x, aux1y, aux1z, f1x, f1y, f1z')
aux2x, aux2y, aux2z, f2x, f2y, f2z = me.dynamicsymbols(
'aux2x, aux2y, aux2z, f2x, f2y, f2z')
aux3x, aux3y, aux3z, f3x, f3y, f3z = me.dynamicsymbols(
'aux3x, aux3y, aux3z, f3x, f3y, f3z')
# Place hlodes for the u_i.diff(t) in the reaction forces
rhs_list = [sm.symbols('rhs' + str(i)) for i in range(14)]
m_e, m_a, rei, reo, shift, La, Le, dist = sm.symbols(
'm_e m_a rei reo shift La Le dist')
k_torque, mu_torque = sm.symbols('k_torque mu_torque')
# rot, rot1 for the kinematical differential equations.
rot, rot1 = [], []
# Explorer body frame
Ae.orient_body_fixed(N, (qex, qey, qez), 'XYZ')
rot.append(Ae.ang_vel_in(N))
Ae.set_ang_vel(N, uex*Ae.x + uey*Ae.y + uez*Ae.z)
rot1.append(Ae.ang_vel_in(N))
# Antenna 0 body frame
Aa0.orient_body_fixed(Ae, (q0x, 0, q0z), 'XYZ')
rot.append(Aa0.ang_vel_in(N))
Aa0.set_ang_vel(Ae, u0x*Aa0.x + u0z*Aa0.z)
rot1.append(Aa0.ang_vel_in(N))
# Antenna 1 body frame
Aa1.orient_body_fixed(Ae, (q1x, 0, q1z), 'XYZ')
rot.append(Aa1.ang_vel_in(N))
Aa1.set_ang_vel(Ae, u1x*Aa1.x + u1z*Aa1.z)
rot1.append(Aa1.ang_vel_in(N))
# Antenna 2 body frame
Aa2.orient_body_fixed(Ae, (0, q2y, q2z), 'XYZ')
rot.append(Aa2.ang_vel_in(N))
Aa2.set_ang_vel(Ae, u2y*Aa2.y + u2z*Aa2.z)
rot1.append(Aa2.ang_vel_in(N))
# Antenna 3 body frame
Aa3.orient_body_fixed(Ae, (0, q3y, q3z), 'XYZ')
rot.append(Aa3.ang_vel_in(N))
Aa3.set_ang_vel(Ae, u3y*Aa3.y + u3z*Aa3.z)
rot1.append(Aa3.ang_vel_in(N))
# Set the points
# Center of gravity of explorer
Aoe.set_pos(O, x*N.x + y*N.y + z*N.z)
Aoe.set_vel(N, ux*N.x + uy*N.y + uz*N.z)
# Points where the antennae attach to the explorer
P0.set_pos(Aoe, dist*Ae.y + shift*Ae.z)
vP0 = P0.v2pt_theory(Aoe, N, Ae)
P0.set_vel(N, vP0 + aux0x*Ae.x + aux0y*Ae.y + aux0z*Ae.z)
P1.set_pos(Aoe, -dist*Ae.y + shift*Ae.z)
vP1 = P1.v2pt_theory(Aoe, N, Ae)
P1.set_vel(N, vP1 + aux1x*Ae.x + aux1y*Ae.y + aux1z*Ae.z)
P2.set_pos(Aoe, dist*Ae.x + shift*Ae.z)
vP2 = P2.v2pt_theory(Aoe, N, Ae)
P2.set_vel(N, vP2 + aux2x*Ae.x + aux2y*Ae.y + aux2z*Ae.z)
P3.set_pos(Aoe, -dist*Ae.x + shift*Ae.z)
vP3 = P3.v2pt_theory(Aoe, N, Ae)
P3.set_vel(N, vP3 + aux3x*Ae.x + aux3y*Ae.y + aux3z*Ae.z)
# Set the mass centers of the antennae
Aoa0.set_pos(P0, La/2 * Aa0.y)
Aoa0.v2pt_theory(P0, N, Aa0)
Aoa1.set_pos(P1, -La/2 * Aa1.y)
Aoa1.v2pt_theory(P1, N, Aa1)
Aoa2.set_pos(P2, La/2 * Aa2.x)
Aoa2.v2pt_theory(P2, N, Aa2)
Aoa3.set_pos(P3, -La/2 * Aa3.x)
Aoa3.v2pt_theory(P3, N, Aa3)
# Set the torques on the antennae
torque0x = -(k_torque * q0x + mu_torque * u0x) * Aa0.x
torque0z = - (k_torque * q0z + mu_torque * u0z) * Aa0.z
torque1x = -(k_torque * q1x + mu_torque * u1x) * Aa1.x
torque1z = - (k_torque * q1z + mu_torque * u1z) * Aa1.z
torque2y = -(k_torque * q2y + mu_torque * u2y) * Aa2.y
torque2z = -(k_torque * q2z + mu_torque * u2z) * Aa2.z
torque3y = -(k_torque * q3y + mu_torque * u3y) * Aa3.y
torque3z = - (k_torque * q3z + mu_torque * u3z) * Aa3.z
torques = [
(Aa0, torque0x + torque0z),
(Aa1, torque1x + torque1z),
(Aa2, torque2y + torque2z),
(Aa3, torque3y + torque3z),
# Reaction torque on explorer
(Ae, -(torque0x + torque0z + torque1x + torque1z +
torque2y + torque2z + torque3y + torque3z)),
# for the reaction forces.
(P0, f0x*Ae.x + f0y*Ae.y + f0z*Ae.z),
(P1, f1x*Ae.x + f1y*Ae.y + f1z*Ae.z),
(P2, f2x*Ae.x + f2y*Ae.y + f2z*Ae.z),
(P3, f3x*Ae.x + f3y*Ae.y + f3z*Ae.z),
]
# Bodies and their inertias
# Explorer is a hollow tube
iXXe = m_e/12 * (3*(rei**2 + reo**2) + Le**2)
iZZe = m_e/2 * (rei**2 + reo**2)
iYYe = iXXe
Inertia_e = me.inertia(Ae, iXXe, iYYe, iZZe)
explorer1 = me.RigidBody('explorer1', Aoe, Ae, m_e, (Inertia_e, Aoe))
# antennea are rods
iRR = 1/12*m_a*La**2
inertia_0 = me.inertia(Aa0, iRR, 0, iRR)
link0 = me.RigidBody('link0', Aoa0, Aa0, m_a, (inertia_0, Aoa0))
inertia_1 = me.inertia(Aa1, iRR, 0, iRR)
link1 = me.RigidBody('link1', Aoa1, Aa1, m_a, (inertia_1, Aoa1))
inertia_2 = me.inertia(Aa2, 0, iRR, iRR)
link2 = me.RigidBody('link2', Aoa2, Aa2, m_a, (inertia_2, Aoa2))
inertia_3 = me.inertia(Aa3, 0, iRR, iRR)
link3 = me.RigidBody('link3', Aoa3, Aa3, m_a, (inertia_3, Aoa3))
bodies = [explorer1, link0, link1, link2, link3]
q_ind = [x, y, z, qex, qey, qez, q0x, q0z, q1x, q1z, q2y, q2z, q3y, q3z]
u_ind = [ux, uy, uz, uex, uey, uez, u0x, u0z, u1x, u1z, u2y, u2z, u3y, u3z]
aux = [aux0x, aux0y, aux0z,
aux1x, aux1y, aux1z,
aux2x, aux2y, aux2z,
aux3x, aux3y, aux3z]
F_r = [f0x, f0y, f0z,
f1x, f1y, f1z,
f2x, f2y, f2z,
f3x, f3y, f3z]
kd = sm.Matrix([
ux - x.diff(t),
uy - y.diff(t),
uz - z.diff(t),
*[(rot[0] - rot1[0]).dot(uv) for uv in Ae],
*[(rot[1] - rot1[1]).dot(uv) for uv in (Aa0.x, Aa0.z)],
*[(rot[2] - rot1[2]).dot(uv) for uv in (Aa1.x, Aa1.z)],
*[(rot[3] - rot1[3]).dot(uv) for uv in (Aa2.y, Aa2.z)],
*[(rot[4] - rot1[4]).dot(uv) for uv in (Aa3.y, Aa3.z)],
])
kanes = me.KanesMethod(
N,
q_ind,
u_ind,
kd,
u_auxiliary=aux,
)
fr, frstar = kanes.kanes_equations(bodies, torques)
eingepraegt = kanes.auxiliary_eqs.subs({i.diff(t): rhs_list[j]
for j, i in enumerate(u_ind)})
Energy and Angular Momentum.
aux_dict = {i: 0 for i in aux}
kin_energy = sum([b.kinetic_energy(N).subs(aux_dict) for b in bodies])
spring_energy = 0.5 * k_torque * (q0x**2 + q0z**2 + q1x**2 + q1z**2 +
q2y**2 + q2z**2 + q3y**2 + q3z**2)
ang_momentum = [
sum([body.angular_momentum(O, N).dot(N.x).subs(aux_dict)
for body in bodies]),
sum([body.angular_momentum(O, N).dot(N.y).subs(aux_dict)
for body in bodies]),
sum([body.angular_momentum(O, N).dot(N.z).subs(aux_dict)
for body in bodies]),
]
Compilation using generate_ode_function.
qL = q_ind + u_ind
pL = [m_e, m_a, rei, reo, dist, shift, La, Le, k_torque, mu_torque]
specified = None
constants = np.array(pL)
loesung = sm.solve(kd, [q_ind[i].diff(t) for i in range(len(q_ind))])
# The solution must be sorted so that it corresponds to KM.q
schluessel = [i.diff(t) for i in kanes.q]
kin_eqs_solved = sm.Matrix([loesung[i] for i in schluessel])
mass_matrix = me.msubs(kanes.mass_matrix, {i: 0 for i in aux})
force = me.msubs(kanes.forcing, {i: 0 for i in aux + F_r})
rhs_gen = generate_ode_function(
force,
kanes.q,
kanes.u,
constants=constants,
mass_matrix=mass_matrix,
specifieds=specified,
coordinate_derivatives=kin_eqs_solved, # rhs of kin. diff. equations
generator='cython',
linear_sys_solver='numpy',
constants_arg_type='array',
specifieds_arg_type='array',
)
# As speed is of no concern here, lambdify is used.
kin_lam = sm.lambdify(qL + pL, kin_energy, cse=True)
spring_lam = sm.lambdify(qL + pL, spring_energy, cse=True)
ang_momentum_lam = sm.lambdify(qL + pL, ang_momentum, cse=True)
eingepraegt_lam = sm.lambdify(F_r + qL + pL + rhs_list,
eingepraegt, cse=True)
Numerical Integration¶
# Input parameters and initial conditions
Le1 = 2.05
rei1 = 0.060
reo1 = 0.076
dist1 = reo1
La1 = 0.56
m_e1 = 13.9
m_a1 = m_e1 / 100.0
shift1 = 0.1
k_torque1 = 0.565
mu_torque1 = 1.13
x1, y1, z1 = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
ux1, uy1, uz1 = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
qex1, qey1, qez1 = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
uez1 = 750.0 * 2 * np.pi / 60 # 750 rpm
uex1 = uez1 / 1.e3
uey1 = uez1 / 1.e3
q0x1, q0z1 = 0.0, 0.0
u0x1, u0z1 = 0.0, 0.0
q1x1, q1z1 = 0.0, 0.0
u1x1, u1z1 = 0.0, 0.0
q2y1, q2z1 = 0.0, 0.0
u2y1, u2z1 = 0.0, 0.0
q3y1, q3z1 = 0.0, 0.0
u3y1, u3z1 = 0.0, 0.0
pL_vals = [m_e1, m_a1, rei1, reo1, dist1, shift1, La1, Le1, k_torque1,
mu_torque1]
y0 = [
x1, y1, z1,
qex1, qey1, qez1,
q0x1, q0z1,
q1x1, q1z1,
q2y1, q2z1,
q3y1, q3z1,
ux1, uy1, uz1,
uex1, uey1, uez1,
u0x1, u0z1,
u1x1, u1z1,
u2y1, u2z1,
u3y1, u3z1,
]
iXXe1 = m_e1/12 * (3*(rei1**2 + reo1**2) + Le1**2)
iZZe1 = m_e1/2 * (rei1**2 + reo1**2)
iYYe1 = iXXe1
print(f'Explorer inertias: Ixx={iXXe1:.6f}, Iyy={iYYe1:.6f}, Izz={iZZe1:.6f}')
def gradient(t, y, args):
# needed for generate_ode_function, if in solve_ivp method != 'RK45'
# y = np.ascontiguousarray(y)
args = np.array(args)
rhs = rhs_gen(y, t, args)
return rhs
interval = 100.0 # seconds
schritte = 1000
times = np.linspace(0., interval, schritte)
t_span = (0., interval)
resultat1 = solve_ivp(gradient, t_span, y0, t_eval=times, args=(pL_vals,),
atol=1e-12, rtol=1e-12,
)
resultat = resultat1.y.T
print('resultat shape', resultat.shape)
print(resultat1.message, '\n')
print(f"To numerically integrate an interval of {interval} sec the "
f"routine cycled {resultat1.nfev:,} times")
Explorer inertias: Ixx=4.900477, Iyy=4.900477, Izz=0.065163
resultat shape (1000, 28)
The solver successfully reached the end of the integration interval.
To numerically integrate an interval of 100.0 sec the routine cycled 1,372,940 times
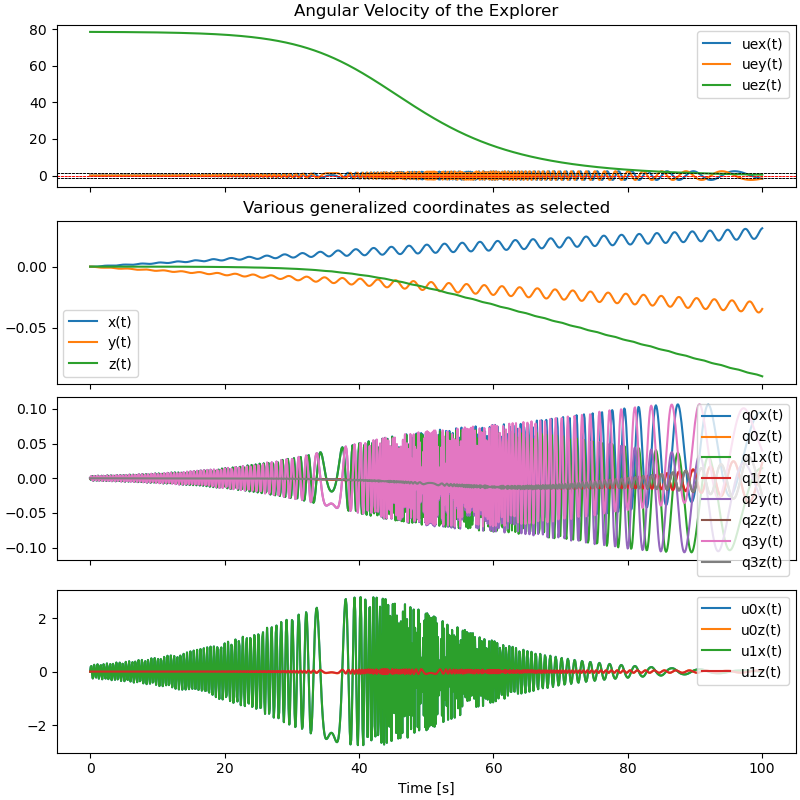
Plot some generalized coordinates
bezeichnung = [str(i) for i in q_ind + u_ind]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(8, 8), layout='constrained',
sharex=True)
for i in (17, 18, 19):
begin = 0
ax[0].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], resultat[begin:, i],
label=bezeichnung[i])
ax[0].axhline(1.35, color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
ax[0].axhline(-1.35, color='black', lw=0.5, ls='--')
ax[0].axhline(0.0, color='red', lw=0.5, ls='--')
ax[0].set_title('Angular Velocity of the Explorer')
_ = ax[0].legend()
for i in (0, 1, 2):
ax[1].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], resultat[begin:, i],
label=bezeichnung[i])
ax[1].set_title('Various generalized coordinates as selected')
_ = ax[1].legend()
for i in (6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13):
ax[2].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], resultat[begin:, i],
label=bezeichnung[i])
_ = ax[2].legend()
for i in (20, 21, 22, 23):
ax[3].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], resultat[begin:, i],
label=bezeichnung[i])
ax[-1].set_xlabel('Time [s]')
_ = ax[3].legend()
Plot Energy and Angular Momentum¶
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(8, 4), layout='constrained', sharex=True)
kin_np = kin_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)
spring_np = spring_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)
total_np = kin_np + spring_np
begin = 0
ax[0].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], kin_np[begin:],
label='kinetic energy')
ax[0].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], spring_np[begin:],
label='spring energy')
ax[0].plot(times[begin: resultat.shape[0]], total_np[begin:],
label='total energy')
ax[0].set_ylabel('Energy [J]')
ax[0].set_title('Energy of the system')
_ = ax[0].legend()
max_x = np.max(ang_momentum_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[0])
may_y = np.max(ang_momentum_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[1])
max_z = np.max(ang_momentum_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[2])
min_x = np.min(ang_momentum_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[0])
min_y = np.min(ang_momentum_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[1])
min_z = np.min(ang_momentum_lam(*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[2])
max_mom = max_x + may_y + max_z
min_mon = min_x + min_y + min_z
error = (max_mom - min_mon) / max_mom
print(f'Max error from conservation of angular momentum: {error:.3e}')
for i, j in enumerate(['x', 'y', 'z']):
ax[1].plot(times[: resultat.shape[0]], ang_momentum_lam(
*(resultat.T), *pL_vals)[i], label=f'angular momentum {j}')
ax[1].set_ylabel('Angular momentum [kg m²/s]')
ax[1].set_title('Angular momentum of the system')
_ = ax[1].legend()
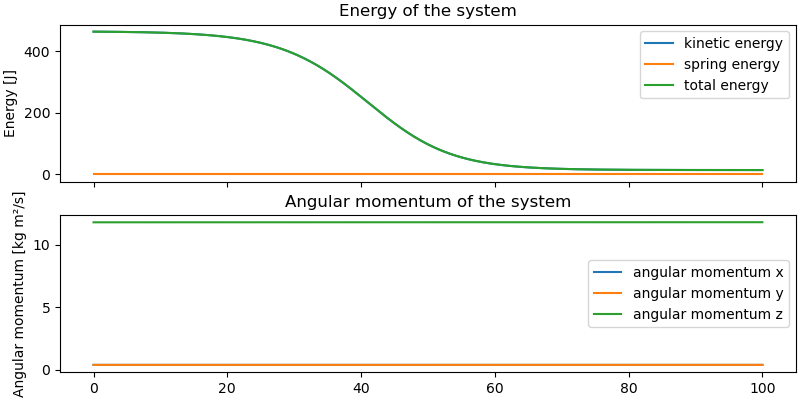
Max error from conservation of angular momentum: 2.866e-03
Calculate Reaction Forces on Points, where the Antennas are attached to Explorer
# Calculate the accelerations needed for the reaction forces. As rhs_gen needs
# C - contiguous arrays, the inputs must be converted here accordingly.
RHS = np.empty((resultat.shape))
pL_vals_C = np.ascontiguousarray(pL_vals)
for i in range(resultat.shape[0]):
res_C = np.ascontiguousarray(resultat[i])
RHS[i] = rhs_gen(res_C, 0.0, pL_vals_C)
reaction_forces = np.empty((resultat.shape[0], 12))
summe_np = np.empty(resultat.shape[0])
def func_react(x0, args):
return eingepraegt_lam(*x0, *args).squeeze()
x0 = np.array([0.0 for _ in range(len(F_r))])
for i in range(resultat.shape[0]):
args = np.array([*resultat[i, :], *pL_vals, *RHS[i, 14:]])
loesung = root(func_react, x0, args=args)
reaction_forces[i, :] = loesung.x
x0 = loesung.x
summe_np[i] = np.sum(loesung.x)
begin = 0
fig, ax = plt.subplots(4, 1, figsize=(8, 8), layout='constrained',
sharex=True)
for i in range(4):
for k, j in zip(reaction_forces[:, 3*i:3*i+3].T, ('x', 'y', 'z')):
ax[i].plot(times[begin:], k[begin:], label=f'Reaction Force {j}')
ax[i].set_ylabel('Force [N]')
ax[i].set_title(f'Reaction Forces at the Antennae Mounting Point P{i} '
'in the Explorer Frame Ae')
ax[i].legend()
_ = ax[-1].set_xlabel('Time [s]')
ax[0].plot(times[begin:], summe_np[begin:], 'r--', label='Sum of all Forces')
_ = ax[0].legend()
Animation using PyDy Visualization¶
In this sphinx environment the animation does not work. The program was left here to show the simplicity of the animation with PyDy Visualization compared to Matplotlib. A screen shot of the animation may be found here: https://github.com/pydy/pst-notebooks the name is explorer1_anomaly.mow
from pydy.viz.shapes import Cylinder, Sphere
from pydy.viz.scene import Scene
from pydy.viz.visualization_frame import VisualizationFrame
# Define the right frames so the cylinders point in the Y direction
Be, Ba0, Ba1, Ba2, Ba3 = sm.symbols('Be B0 B1 B2 B3', cls=me.ReferenceFrame)
# Point to see easily how explorer is turning.
P_red = me.Point('P_red')
Be.orient_body_fixed(Ae, (-np.pi/2, 0, 0), 'XYZ')
Ba1.orient_body_fixed(Aa1, (0, 0, np.pi), 'XYZ')
Ba2.orient_body_fixed(Aa2, (0, 0, np.pi/2), 'XYZ')
Ba3.orient_body_fixed(Aa3, (0, 0, -np.pi/2), 'XYZ')
P_red.set_pos(Aoe, Le/4 * Be.y + reo * Be.z)
farben = ['grey', 'blue', 'green', 'red', 'yellow']
viz_frames = []
mass_centers = [Aoe, Aoa0, Aoa1, Aoa2, Aoa3]
frames = [Ae, Aa0, Ba1, Ba2, Ba3]
for i, antenna in enumerate(bodies[1:]):
antenna_shape = Cylinder(name='antenna{}'.format(i),
radius=0.025,
length=La1,
color=farben[i])
viz_frames.append(VisualizationFrame('antenna_frame{}'.format(i),
frames[i+1],
mass_centers[i+1],
antenna,
antenna_shape))
explorer_shape = Cylinder(name='explorer',
radius=reo1,
length=Le1,
color=farben[0])
viz_frames.append(VisualizationFrame('explorer_frame',
Be,
mass_centers[0],
explorer1,
explorer_shape))
P_red_shape = Sphere(name='red_sphere',
radius=0.05,
color='red')
viz_frames.append(VisualizationFrame('red_sphere_frame',
Be,
P_red,
P_red,
P_red_shape))
scene = Scene(N, O, *viz_frames)
# Provide the data to compute the trajectories of the visualization frames.
scene.times = times
scene.constants = dict(zip(pL, pL_vals))
scene.states_symbols = q_ind + u_ind
scene.states_trajectories = resultat
# scene.display_jupyter(axes_arrow_length=20)
Animation with Matplotlib¶
fps = 10
# Create the end points of the antennas
P01, P11, P21, P31, omega = sm.symbols('P01 P11 P21 P31 omega', cls=me.Point)
P01.set_pos(P0, La * Aa0.y)
P11.set_pos(P1, -La * Aa1.y)
P21.set_pos(P2, La * Aa2.x)
P31.set_pos(P3, -La * Aa3.x)
omega.set_pos(Aoe, uex*Ae.x + uey*Ae.y + uez*Ae.z)
coordinates = Aoe.pos_from(O).to_matrix(N)
for point in (P0, P01, P1, P11, P2, P21, P3, P31, omega):
coordinates = coordinates.row_join(point.pos_from(O).to_matrix(N))
coordinates_lam = sm.lambdify(qL + pL, coordinates, cse=True)
t_arr = np.linspace(0, interval, schritte)
state_sol = CubicSpline(t_arr, resultat)
# cylinder generation
def make_cylinder_mesh(Le, reo, n_theta=48, n_z=10):
# Create a cylinder mesh centered at origin along the z-axis:
# - z in [-Le/2, +Le/2]
# - radius = reo
# Returns X,Y,Z arrays shaped (n_z, n_theta)
theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n_theta)
z = np.linspace(-Le/2, Le/2, n_z)
Theta, Z = np.meshgrid(theta, z)
X = reo * np.cos(Theta)
Y = reo * np.sin(Theta)
return X, Y, Z
# Rotation matrices
def Rx(angle):
c, s = np.cos(angle), np.sin(angle)
return np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, c, -s],
[0, s, c]])
def Ry(angle):
c, s = np.cos(angle), np.sin(angle)
return np.array([[c, 0, s],
[0, 1, 0],
[-s, 0, c]])
def Rz(angle):
c, s = np.cos(angle), np.sin(angle)
return np.array([[c, -s, 0],
[s, c, 0],
[0, 0, 1]])
# Apply transform
def transform_cylinder(X, Y, Z, Aoe, qx, qy, qz):
# Apply rotation (qx,qy,qz) and translation Aoe to the mesh.
# Rotation order: Rx then Ry then Rz => R = Rz @ Ry @ Rx
# flatten points for matrix multiplication
pts = np.vstack((X.ravel(), Y.ravel(), Z.ravel())) # shape (3, N)
# Build rotation matrix according to selected convention
R = Rz(qz) @ Ry(qy) @ Rx(qx)
pts_rot = R @ pts
pts_rot[0, :] += Aoe[0]
pts_rot[1, :] += Aoe[1]
pts_rot[2, :] += Aoe[2]
Xr = pts_rot[0, :].reshape(X.shape)
Yr = pts_rot[1, :].reshape(Y.shape)
Zr = pts_rot[2, :].reshape(Z.shape)
return Xr, Yr, Zr
def init():
Le = Le1 # length
reo = reo1 # radius
X, Y, Z = make_cylinder_mesh(Le, reo, n_theta=16, n_z=8)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.set_box_aspect([1, 1, 1]) # make aspect equal
L = 1.5
ax.set_xlim(-L, L)
ax.set_ylim(-L, L)
ax.set_zlim(-L, L)
ax.set_xlabel('X [m]', fontsize=15)
ax.set_ylabel('Y [m]', fontsize=15)
ax.set_zlabel('Z [m]', fontsize=15)
# initial pose
coords = coordinates_lam(*state_sol(0), *pL_vals)
Aoe0 = np.array([coords[0, 0], coords[1, 0], coords[2, 0]])
qx0, qy0, qz0 = state_sol(0)[3:6] # explorer angles
Xr, Yr, Zr = transform_cylinder(X, Y, Z, Aoe0, qx0, qy0, qz0)
surf = ax.plot_surface(Xr, Yr, Zr, rstride=2, cstride=2, linewidth=0,
alpha=0.7, color='grey')
antenna0, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=2)
antenna1, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=2)
antenna2, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=2)
antenna3, = ax.plot([], [], [], color='black', lw=2)
pfeil1 = ax.quiver(coords[0, 0], coords[1, 0], coords[2, 0],
(coords[0, 9] - coords[0, 0]),
(coords[1, 9] - coords[1, 0]),
(coords[2, 9] - coords[2, 0]), color='red',
arrow_length_ratio=0.3,)
return (fig, ax, surf, antenna0, antenna1, antenna2, antenna3, pfeil1,
X, Y, Z)
fig, ax, surf, antenna0, antenna1, antenna2, antenna3, pfeil1, X, Y, Z = init()
def update(t):
global surf, pfeil1
# remove previous surface and omega
surf.remove()
pfeil1.remove()
ax.set_title(f"Running time: {t:.2f} sec \n The red arrow shows the "
f"direction of the angular velocity \n "
f"vector of the explorer", fontsize=15)
coords = coordinates_lam(*state_sol(t), *pL_vals)
# create explorer
Aoe = np.array([coords[0, 0], coords[1, 0], coords[2, 0]])
qx, qy, qz = state_sol(t)[3:6] # explorer angles
Xr, Yr, Zr = transform_cylinder(X, Y, Z, Aoe, qx, qy, qz)
surf = ax.plot_surface(Xr, Yr, Zr, rstride=2, cstride=2, linewidth=0,
alpha=0.8, color='grey')
antenna0.set_data([coords[0, 1], coords[0, 2]],
[coords[1, 0], coords[1, 1]])
antenna0.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 0], coords[2, 1]])
antenna1.set_data([coords[0, 3], coords[0, 4]],
[coords[1, 3], coords[1, 4]])
antenna1.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 3], coords[2, 4]])
antenna2.set_data([coords[0, 5], coords[0, 6]],
[coords[1, 5], coords[1, 6]])
antenna2.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 5], coords[2, 6]])
antenna3.set_data([coords[0, 7], coords[0, 8]],
[coords[1, 7], coords[1, 8]])
antenna3.set_3d_properties([coords[2, 7], coords[2, 8]])
# As the angular velocity change substantially over time, it is scaled
# to be visible in the plot at all times.
scale_factor = 2.0 / np.sqrt((coords[0, 9] - coords[0, 0])**2 +
(coords[1, 9] - coords[1, 0])**2 +
(coords[2, 9] - coords[2, 0])**2)
pfeil1 = ax.quiver(coords[0, 0], coords[1, 0], coords[2, 0],
scale_factor * (coords[0, 9] - coords[0, 0]),
scale_factor * (coords[1, 9] - coords[1, 0]),
scale_factor * (coords[2, 9] - coords[2, 0]),
color='red', arrow_length_ratio=0.2)
return surf, antenna0, antenna1, antenna2, antenna3, pfeil1
frames = np.concatenate((np.arange(0.0, 0.05 * interval, 1 / fps),
np.arange(0.9 * interval, 0.95 * interval, 1 / fps)))
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=frames, interval=1000 / fps,
blit=False)
plt.show()