Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Zermelo’s Problem (betts-10-148)¶
This is example 10.148 from John T. Betts, Practical Methods for Optimal Control Using NonlinearProgramming, 3rd edition, Chapter 10: Test Problems. The goal is to minimize the final time \(t_f\) to reach the point (0 / 0), having started at the point (3.5 / -1.8).
More information about Zermelo’s navigation problem can be found at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zermelo%27s_navigation_problem
States
\(x, y\) : state variables
Controls
\(\theta\) : control variable
import numpy as np
import sympy as sm
import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
import time
from opty import Problem
from opty.utils import MathJaxRepr
Equations of motion.
t = me.dynamicsymbols._t
x, y = me.dynamicsymbols('x, y')
theta = me.dynamicsymbols('theta')
h = sm.symbols('h')
V, c = sm.symbols('V, c')
eom = sm.Matrix([
-x.diff(t) + V*sm.cos(theta) + c*y,
-y.diff(t) + V*sm.sin(theta),
])
MathJaxRepr(eom)
Define and Solve the Optimization Problem¶
num_nodes = 2001
t0 = 0*h
tf = (num_nodes - 1) * h
interval_value = h
state_symbols = (x, y)
unkonwn_input_trajectories = (theta, )
par_map = {V: 1.0, c: -1.0}
Specify the objective function and form the gradient.
def obj(free):
return free[-1]
def obj_grad(free):
grad = np.zeros_like(free)
grad[-1] = 1.0
return grad
Set the instance constraints. Forcing \(h \geq 0\) will avoid physically meaninigless negative time intervals.
instance_constraints = (
x.func(t0) - 3.5,
y.func(t0) + 1.8,
x.func(tf),
y.func(tf),
)
bounds = {
h: (0.0, 0.5),
}
Create the optimization problem and set any options.
prob = Problem(
obj,
obj_grad,
eom,
state_symbols,
num_nodes,
interval_value,
instance_constraints=instance_constraints,
known_parameter_map=par_map,
bounds=bounds,
time_symbol=t,
)
Give some rough estimates for the trajectories.
initial_guess = np.ones(prob.num_free) * 0.1
Find the optimal solution.
start_time = time.time()
solution, info = prob.solve(initial_guess)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"Solving time: {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
print(info['status_msg'])
Jstar = 5.26493205
print(f"Objective value achieved: {(num_nodes-1)*info['obj_val']:.4f} ",
f"as per the book it is {Jstar:.4f}, so the error is: "
f"{((num_nodes-1)*info['obj_val'] - Jstar)/Jstar*100:.3f} % ")
Solving time: 3.42 seconds
b'Algorithm terminated successfully at a locally optimal point, satisfying the convergence tolerances (can be specified by options).'
Objective value achieved: 5.2637 as per the book it is 5.2649, so the error is: -0.023 %
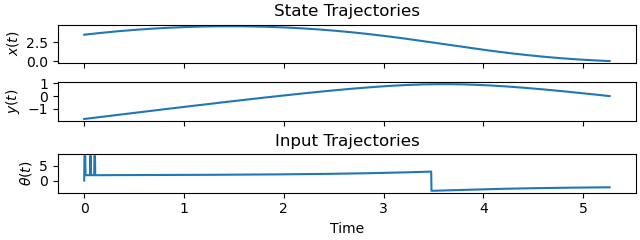
Plot the optimal state and input trajectories.
_ = prob.plot_trajectories(solution)
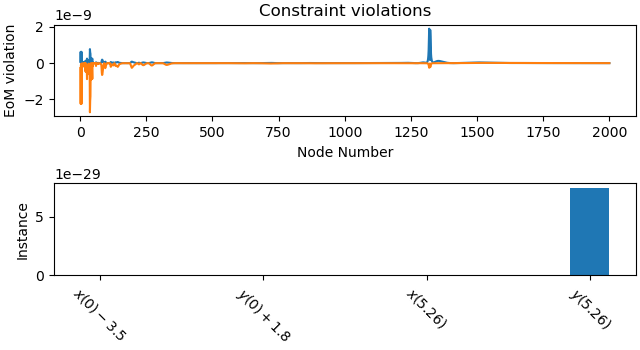
Plot the constraint violations.
_ = prob.plot_constraint_violations(solution)
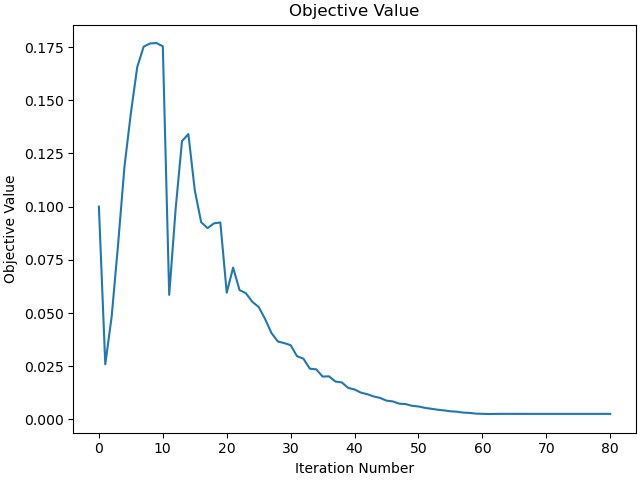
Plot the objective function as a function of optimizer iteration.
_ = prob.plot_objective_value()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 11.363 seconds)