Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Van der Pol Oscillator (Betts 10.144 / 145)¶
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Van_der_Pol_oscillator
These are examples 10.144 / 145 from John T. Betts, Practical Methods for Optimal Control Using NonlinearProgramming, 3rd edition, Chapter 10: Test Problems. It is described in more detail in section 4.14. example 4.11 of the book.
Note¶
A rather high number of nodes is required to get a good solution. Maybe an indication that the problem is stiff.
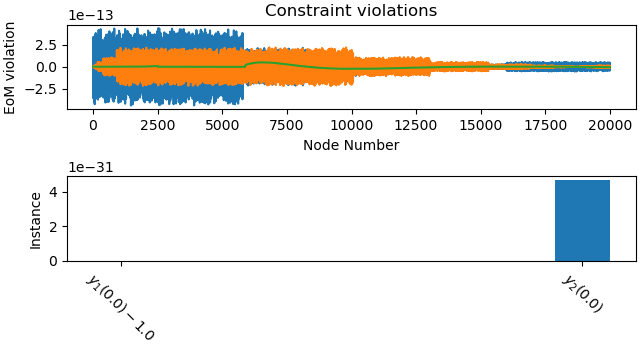
Both formulations give very similar results.
import numpy as np
import sympy as sm
import sympy.physics.mechanics as me
import time
from opty.direct_collocation import Problem
from opty.utils import create_objective_function, MathJaxRepr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
First version of the problem (10.144)¶
States
\(y_1, y_2\) : state variables
Controls
\(u\) : control variables
Equations of Motion.¶
t = me.dynamicsymbols._t
y1, y2 = me.dynamicsymbols('y1, y2')
u = me.dynamicsymbols('u')
eom = sm.Matrix([
-y1.diff() + y2,
-y2.diff(t) + (1 - y1**2)*y2 - y1 + u,
])
MathJaxRepr(eom)
Define and Solve the Optimization Problem.¶
num_nodes = 20001
t0, tf = 0.0, 5.0
interval_value = (tf - t0) / (num_nodes - 1)
state_symbols = (y1, y2)
unkonwn_input_trajectories = (u, )
objective = sm.integrate(u**2 + y1**2 + y2**2, t)
obj, obj_grad = create_objective_function(
objective,
state_symbols,
unkonwn_input_trajectories,
tuple(),
num_nodes,
interval_value,
time_symbol=t
)
instance_constraints = (
y1.func(t0) - 1.0,
y2.func(t0),
)
bounds = {
y2: (-0.4, np.inf),
}
prob = Problem(
obj,
obj_grad,
eom,
state_symbols,
num_nodes,
interval_value,
instance_constraints=instance_constraints,
bounds=bounds,
time_symbol=t,
)
Solve the optimization problem. Give some rough estimates for the trajectories.
initial_guess = np.ones(prob.num_free)
Find the optimal solution.
start = time.time()
solution, info = prob.solve(initial_guess)
end = time.time()
print(f"Solving took {end - start:.2f} seconds.")
print(info['status_msg'])
Jstar = 2.95369916
print(f"Objectve is: {info['obj_val']:.8f}, " +
f"as per the book it is {Jstar}, so the deviation is: "
f"{(info['obj_val'] - Jstar) / Jstar * 100:.5e} %")
Solving took 4.67 seconds.
b'Algorithm terminated successfully at a locally optimal point, satisfying the convergence tolerances (can be specified by options).'
Objectve is: 2.95319329, as per the book it is 2.95369916, so the deviation is: -1.71266e-02 %
Store the first solution for later comparison.
solution1 = solution
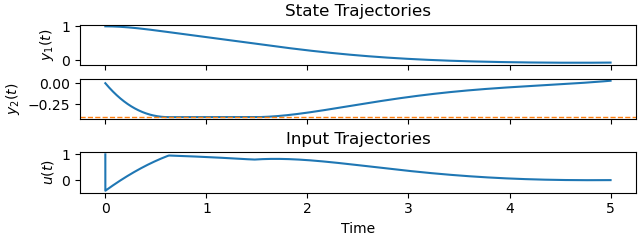
Plot the optimal state and input trajectories.
_ = prob.plot_trajectories(solution, show_bounds=True)
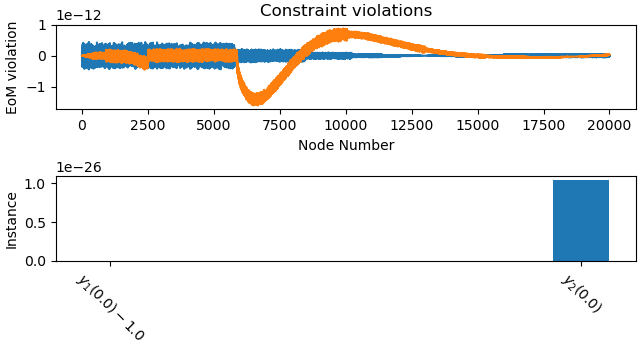
Plot the constraint violations.
_ = prob.plot_constraint_violations(solution)
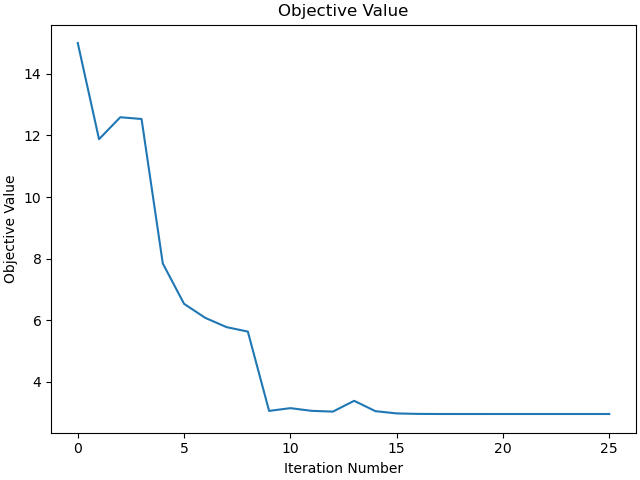
Plot the objective function as a function of optimizer iteration.
_ = prob.plot_objective_value()
Second version of the problem (10.145)¶
It is same as problem 10.144 but reformulated. It has two control variables and one additional algebraic equation of motion.
States
\(y_1, y_2\) : state variables
Controls
\(u, v\) : control variables
Equations of Motion.¶
y1, y2, v = me.dynamicsymbols('y1, y2, v')
u = me.dynamicsymbols('u')
eom = sm.Matrix([
-y1.diff() + y2,
-y2.diff(t) + v - y1 + u,
v - (1-y1**2)*y2,
])
MathJaxRepr(eom)
Define and Solve the Optimization Problem¶
state_symbols = (y1, y2)
unkonwn_input_trajectories = (u, v)
objective = sm.integrate(u**2 + y1**2 + y2**2, t)
obj, obj_grad = create_objective_function(
objective,
state_symbols,
unkonwn_input_trajectories,
tuple(),
num_nodes,
interval_value
)
instance_constraints = (
y1.func(t0) - 1.0,
y2.func(t0),
)
bounds = {
y2: (-0.4, np.inf),
}
prob = Problem(
obj,
obj_grad,
eom,
state_symbols,
num_nodes,
interval_value,
instance_constraints=instance_constraints,
bounds=bounds,
time_symbol=t,
)
Solve the optimization problem. Give some rough estimates for the trajectories.
initial_guess = np.ones(prob.num_free)
Find the optimal solution.
start = time.time()
solution, info = prob.solve(initial_guess)
end = time.time()
print(f"Solving took {end - start:.2f} seconds.")
Jstar = 2.95369916
print(f"Objectve is: {info['obj_val']:.8f}, " +
f"as per the book it is {Jstar}, so the deviation is: "
f"{(info['obj_val'] - Jstar) / Jstar * 100:.5e} %")
Solving took 6.36 seconds.
Objectve is: 2.95319329, as per the book it is 2.95369916, so the deviation is: -1.71266e-02 %
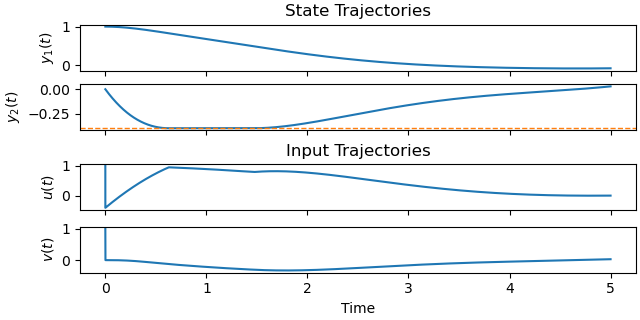
Plot the optimal state and input trajectories.
_ = prob.plot_trajectories(solution, show_bounds=True)
Plot the constraint violations.
_ = prob.plot_constraint_violations(solution)
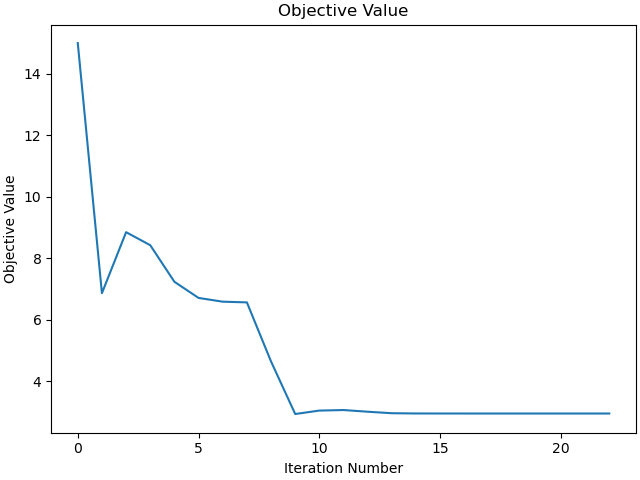
Plot the objective function as a function of optimizer iteration.
_ = prob.plot_objective_value()
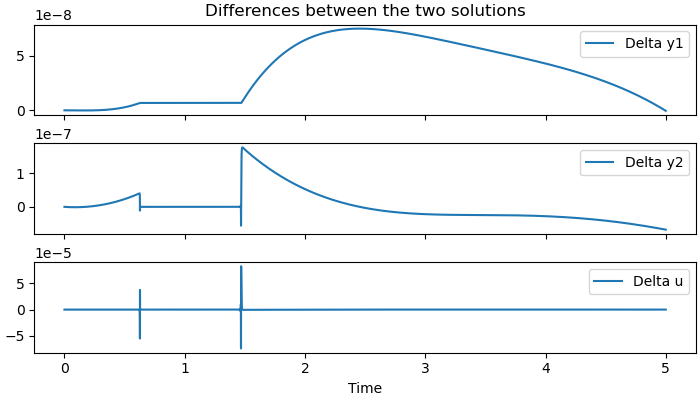
Plot the Difference between the two Solutions.¶
diffy1 = solution1[: num_nodes] - solution[: num_nodes]
diffy2 = solution1[num_nodes: 2*num_nodes] - solution[num_nodes: 2*num_nodes]
diffu = solution1[2*num_nodes:] - solution[2*num_nodes: 3*num_nodes]
times = np.linspace(t0, tf, num_nodes)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(7, 4), sharex=True,
constrained_layout=True)
ax[0].plot(times, diffy1, label='Delta y1')
ax[0].legend()
ax[1].plot(times, diffy2, label='Delta y2')
ax[1].legend()
ax[2].plot(times, diffu, label='Delta u')
ax[2].legend()
ax[2].set_xlabel('Time')
_ = ax[0].set_title('Differences between the two solutions')
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 27.031 seconds)